Cookbook
4-m MOSAIC II CCD Imager COOKBOOK
A. Kunder 2010, modified from K. Olson 2003
DON'T PANIC !!
Set Up
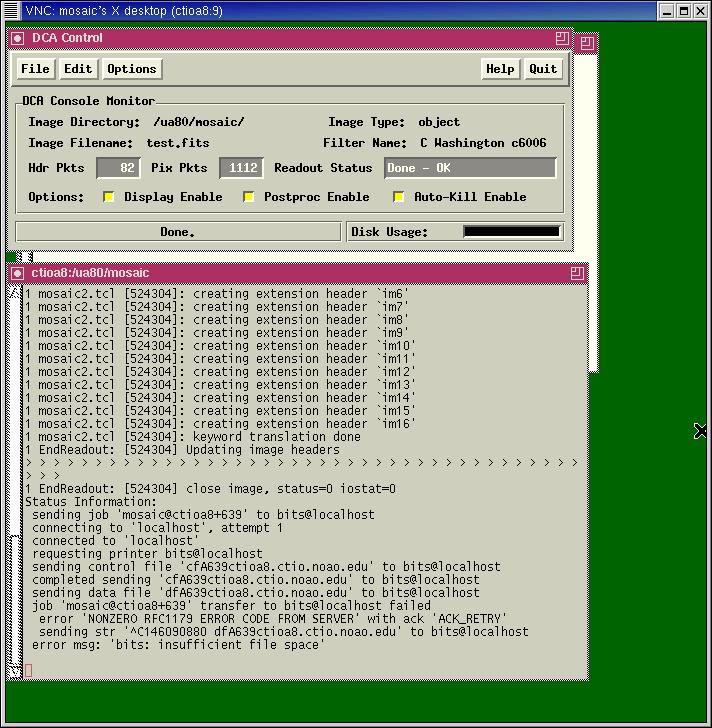
Three windows that look like the images below should be on your screen. These are virtual desktops. ctioa0 runs the camera electronics and ctioa8 accepts and stores the images. Do not use the observing desktop for anything other than taking observations! (Why? The observing desktop runs on ctioa1, which is a very old machine. Your data are transferred to ctioa8 automatically by the DCA. If you type e.g. "display obj001.fits 1" in the Arcon window, you are asking ctioa1's slooow CPU to display an image that it accesses across the network. Bad idea!).
The following images show the VNC windows:
- You are sitting in front of ctioa8, the Mosaic II observing computer. An observer support person (Alberto Alvarez or Claudio Aguilera) has probably already set up the instrument for your observing program. It would be good to verify the setup:
- There are five parameter files you will need to check out. Since Arcon uses an IRAF interface, these are IRAF parameter files:
- obspars
- instrpars
- wheel1
- detpars
- telpars
Typing "lpar obspars" will list the contents of obspars, for example, while simply typing "obspars" or "epar obspars" will allow you to edit the values. The exception to this last statement is detpars: to edit detpars, DO NOT type "detpars" or "epar detpars"--you must instead type "setdet force+", so as to ensure that your changes are updated in the instrument.
- Now that you have set up the Arcon environment, take a look at the MCCD Configuration window. Are there green check marks by the words "TCS" and "MSE"? If either of these are highlighted in red, you'll need to contact observer support (x420). Likewise, if any of the temperature indicators (Dewar, Fill neck, or CCD) are red, there may be a problem-- contact observer support. There should be a thick red line at the top of the window, indicating that the shutter is closed. There should also be two green arrows between the shutter graphic and the blue line indicating the filter, which means that light is getting to the guide cameras.
Taking exposures -- Getting Started
- Make a directory to store your data.
In the Arcon Acquisition window, go to the mosaic directory on one of the free disks on ctioa8 (e.g. /ua83/mosaic, /ua84/mosaic,/ua85/mosaic--NOT /ua80/mosaic), make yourself a subdirectory, and cd to it. Make sure you cd into this directory in the xgterm located on catioa8.
- Check that you have enough space.
Type "df -h" and make sure you have at least 15 GB per night. If you need more space, talk to one of the support people.
- Restart ARCON
This should be done once every 24 hours to minimize arcon crashes. Follow the restart arcon procedure.
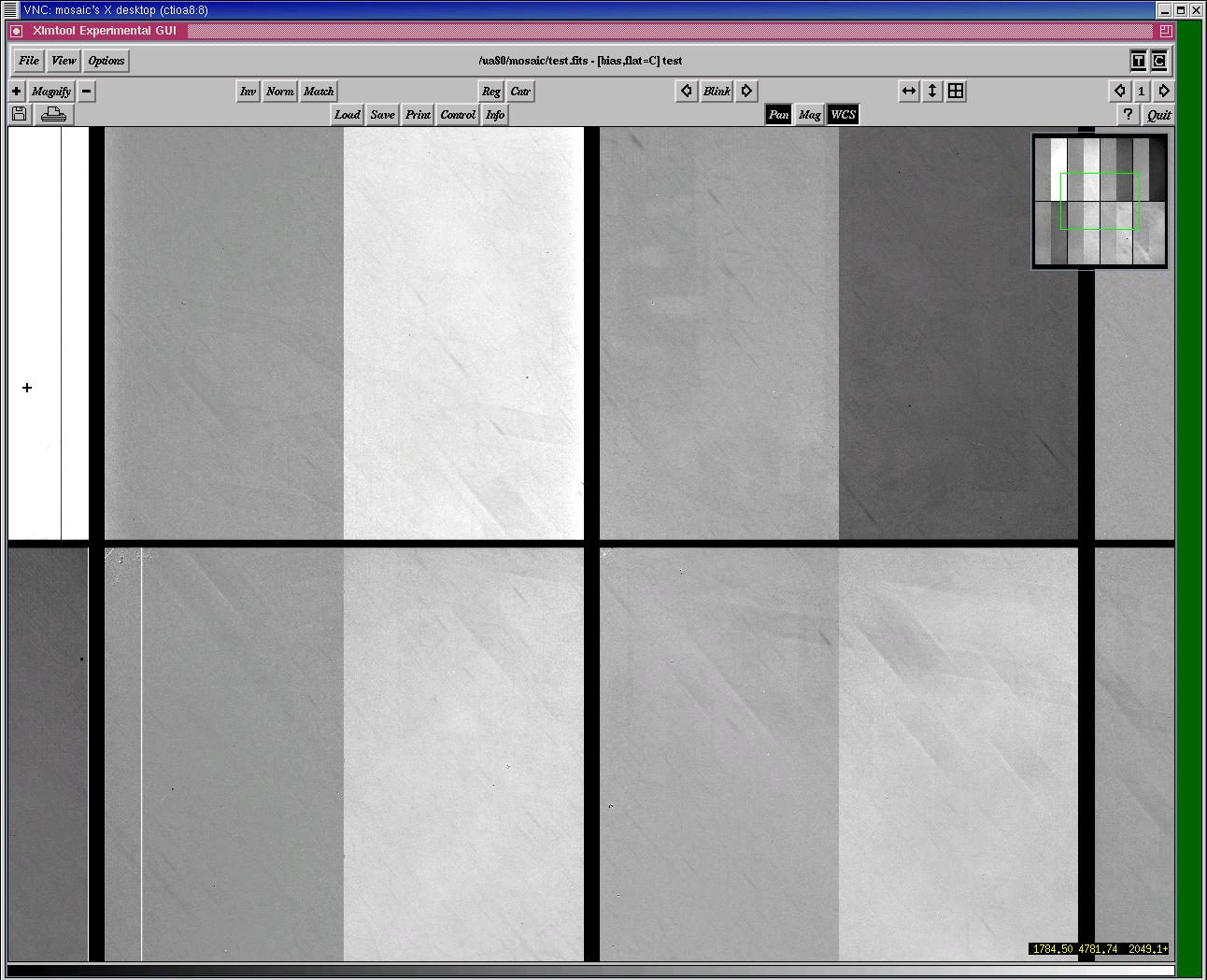
- Take a test exposure by typing "test", specify that you want to take a "zero" frame. As the bias frame reads out, watch the Arcon status window, the DCA windows, and the real time display (RTD). Are the "Buffers read" in the Arcon status window ticking over? Are the "Pix Pkts" changing in the DCA control window in time with the "Buffers read"? Is the image appearing on the RTD? Once the zero frame is read out, does it look more or less like this? If there are nasty-looking patterns in your zero frame, take a few more to see if they go away. If not, then contact observer support.
- Take more zeros by typing "zero" or "observe" and then "zero" (make sure that the dome is dark for this).
- Take flats.
Ask the night assistant or observer support to point the telescope at the white spot and turn on the flat field lamps. Take ~6 dome flats through each filter, using the exposure times listed on the board. You can simply type "dflat". The command "doobs" will make taking flats easier, once you've taken one exposure through each filter to verify that the exposure times are right (using the "observe" command or simply the "dflat" command). You don't want more than 10000 counts in your flats, since the saturation levels for some of the CCDs are ~20000. If the standard dome flat exposure times produce fewer than ~10000 counts, then the dome lamps may be misaligned or one or more may have burned out. Please ask observer support to check the dome lamps if this is the case.
Taking exposures -- Observing your targets
- Observer support will open the dome 1 hour before sunset to clear the air out of the dome.
- Take twilight sky flats right after sunset.
Ask the night assistant to point the telescope 1-2 hours to the east. Type "sflat" and take 1-second exposures, starting with the filter that you expect will require the brightest illumination, until the counts drop to ~10000. Use "sflat" to take successive sky flat exposures, asking the night assistant to move the telescope E by 30 arcseconds between exposures. With the 100-second readout time, you will need to increase your exposure time by a factor of ~1.5 between exposures to maintain the same count level.
- Pointing.
Once it is too dark for twilight sky flats, ask the night assistant to move to a bright star to zero point the telescope. Take a 1-second "test" object exposure. In the xgterm on ctioa8, type
"mscdisp test zrange- zscale - z1=1000 z2=50000"
Calculate the offset needed to bring the star to the center (the pixel scale is 0.27 arcsec/pix), by then typing
"zpt"
Then move the mouse on the center of the star and hit the space bar. The teloffset values will be read out in the xgterm. You can have the night assistant do this offset, or you can do it yourself by typing
"teloffset RA_offset_arcsec DEC_offset_arcsec"
command in the Arcon Aquistion box. Bear in mind that DEC increases with X and RA with Y. Take another 1-second test to verify that you moved the telescope in the right direction, and by the right amount.
- Focus.
Start the focus procedure by typing
"settemp"
--this command reads the temperature of the upper truss and records it in the "temperature" parameter of instrpars, described above. It also takes a guess at the best focus value--use this value as the focus value of the middle of your sequence. Now type
"focus"
specify an exposure time of 5-15 sec, and use the R filter (if you use another filter to do the focus, bear in mind that Arcon will add the focus offset listed in wheel1 to the focus when taking an exposure). Using the parameter values specified in telpars, Arcon will now take a sequence of N exposures, stepping the focus and shifting the charge by a number of rows between each one. After the exposure is done reading out, you will see an image containing columns of stars on the RTD. It will look something like this and like this if you zoom in.
In an IRAF window on ctioa8, type
"mscfocus"
You will now select stars to use in calculating the best focus. Place the cursor on the top star in a cleanly separated, unsaturated sequence and type the "g" key (always use the top star, regardless of whether or not there is a double step between it and its neighbor). A window will appear displaying the FWHM as a function of focus for that star. Type "q", place the cursor on the top star of another column, and type "g" again. Repeat this sequence until you have measured the focus profiles of 1-2 stars on each CCD. With the cursor in the ximtool, finally type "q". You will now see a window overlaying the focus sequences for all of the stars you just measured. If there are strongly outlying points, place the cursor on them and type "d", which deletes the information for the whole star associated with that point, Once you are satisfied, type "q", and the program calculates the best focus for you.
In mscfocus, you might prefer to use the "m" key (again always use the top star). Hit the "m" key for stars in all the different CCDs. When you have sampled a sufficient quantity, hit "q". You will get something like this:
image here
Note the best focus value and fwhm, which is displayed on the top of the pop-up window.
Enter the best focus value in the "basefocus" parameter in instrpars, and change "reftemp" to equal the value in "temperature". If "setfocus" is set to "auto", Arcon will calculate the difference between "temperature" and "reftemp", multiply this by the temperature coefficient, and add it to "basefocus" before taking an image. Until you type "settemp" again, this focus adjustment will be 0. Later during the night, if you find that the temperature has changed significantly, type "settemp" before taking an exposure, and "temperature" will be updated.
If you don't like using "mscfocus", you can always use "mscexam" instead. "mscexam" works just like "imexam"--you can examine stars with the "r" or "e" key to pick which of the stars in the focus sequence is in best focus.
- Focus on the fly: Do an "mscexam" and hit "m". If the resulting profile looks North-South elongated like this:
image here
then you must decrease the focus value. If the profile looks East-West, incrase the focus value.
End Of The Night
- Your observing assistant will close the dome, fill the dewar, etc.
- At the end of the night, please fill out the Blanco 4-m Night Report (Internal Access Only)
- Your night lunch form is due at 2:00 PM, but if you don't wake up in time, usually the kitchen staff is merciful.
Observing tips
- To help identify your targets, here is a schematic of the orientation of Mosaic 2:
image here
- For taking dither sequences to remove the gap signature, "mosdither" is a useful command. Type "epar modither" to look at its parameters. The files characterizing various dither sequences are stored in /ua80/mosaic/dithers/. You will need a 5-point dither to cover all areas with at least 3 images.
- If your program involves a large number of short exposures, then "mosocs" could save you a lot of time. See the MOSOCS documentation for help.
- If Arcon or the DCA crash, check to make sure that /tmp on ctioa0 isn't filling up with *xpim* files. If it fills up, the only recourse is to reboot ctioa0.
- Type the command "settemp" frequently to update the focus value.
Updated on May 23, 2022, 11:05 am