Orion
Origin
Orion is a prominent constellation during winter in the northern hemisphere. As it lies near the celestial equator, it is visible from most of the world. It is one of the 88 modern constellations and was among the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is named for a mythological hunter in Greek mythology. The Sumerians saw Orion as Gilgamesh fighting a bull, Taurus.
Bright Stars
Orion's seven brightest stars form a distinctive hourglass-shaped asterism, or pattern, in the night sky. Four stars — Rigel, Betelgeuse, Bellatrix, and Saiph — form a large, roughly rectangular shape, at the center of which lie the three stars of Orion's Belt — Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. His head is marked by an additional eighth star called Meissa, which is fairly bright to the observer. Descending from the ‘belt’ is a smaller line of three stars, Orion's sword (the middle of which is in fact not a star but the Orion Nebula), also known as the hunter's sword.
Many of the stars are luminous hot blue supergiants, with the stars of the belt and sword forming the Orion OB1 association. Standing out by its red hue, Betelgeuse may nevertheless be a runaway member of the same group.
- Betelgeuse, also designated Alpha Orionis, is a massive red supergiant star. It is the second brightest star in Orion, and is a semiregular variable star.
- Rigel, also known as Beta Orionis, is the sixth-brightest star in the night sky.
- Bellatrix is designated Gamma Orionis and is the twenty-seventh-brightest star in the night sky.
- Mintaka is designated Delta Orionis and is the faintest of the three stars in Orion's Belt. Its name means ‘the belt’.
- Alnilam is designated Epsilon Orionis and is named for the Arabic phrase meaning string of pearls. It is the middle and brightest of the three stars of Orion's Belt.
- Alnitak, meaning ‘’the girdle’, is designated Zeta Orionis. It is a triple star system.
- Saiph is designated Kappa Orionis by Bayer, It means ‘the sword of the giant’.
- Meissa is designated Lambda Orionis is one of the stars that forms Orion's head. Its name means ‘the "shining one’. It is a multiple star with an apparent magnitude of 3.33.
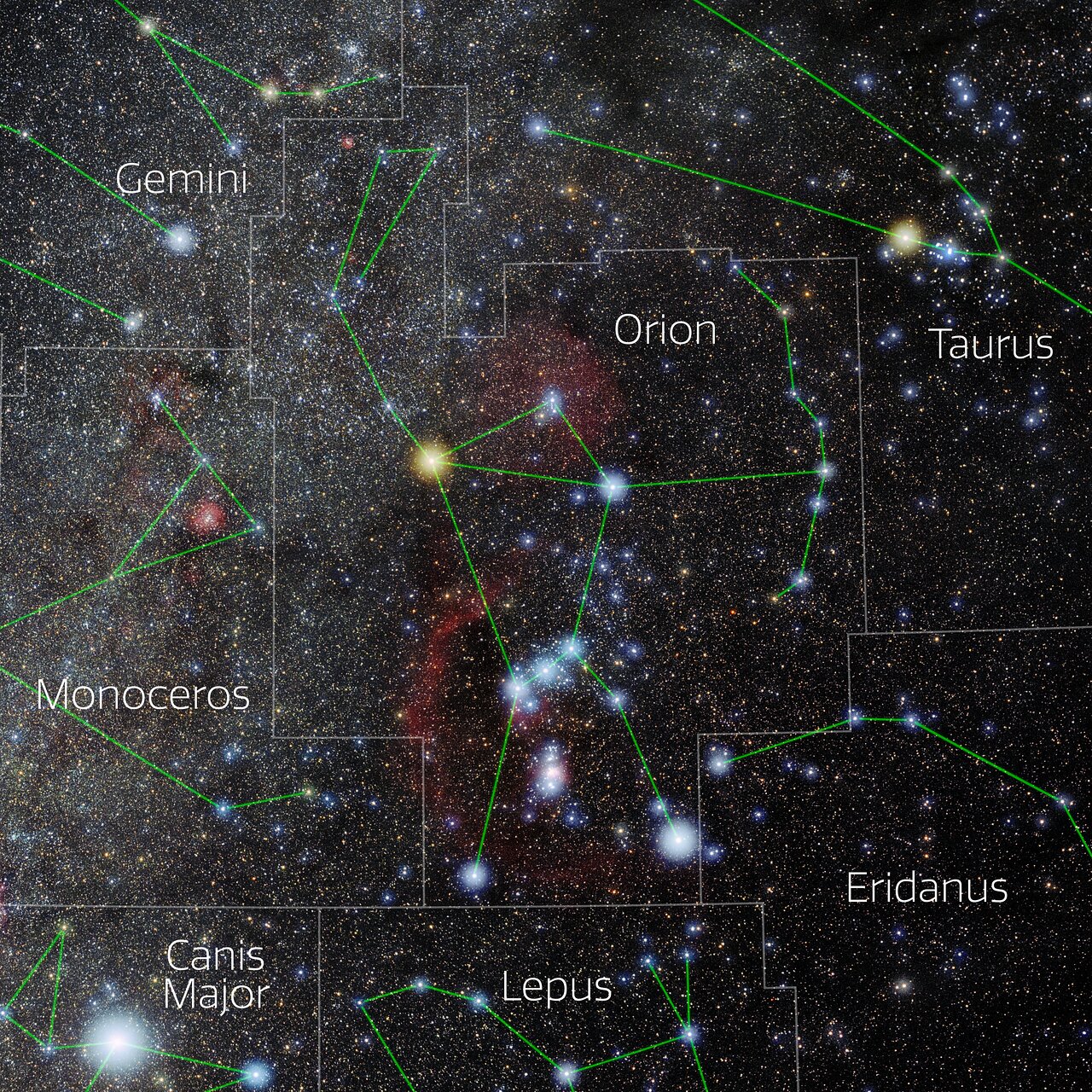

 Photo of the constellation Orion produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Photo of the constellation Orion produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Credit: E. Slawik/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani
Notable Objects
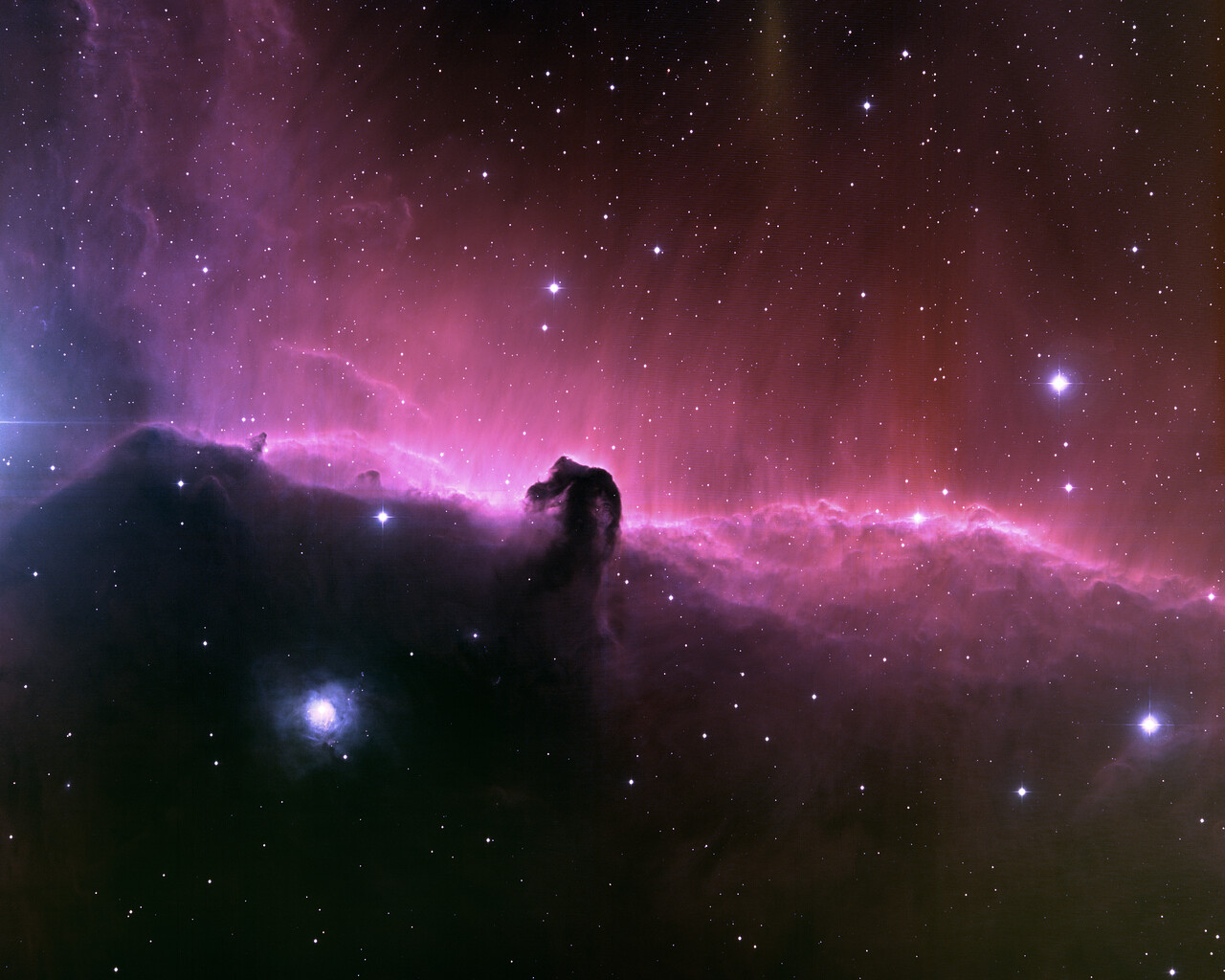
Messier 42 is the famous Orion Nebula, a nearby and massive star forming region, about 1200 light-years away. The Orion Nebula is pleasing to observe through binoculars and telescopes. Messier 78 is a reflection nebula in Orion about 1400 light-years away and shining at magnitude 8.3. NGC 1999 is another reflection nebula about 1500 light-years distant and shining at magnitude 10.5. IC434 is better known as the Horsehead Nebula. The Horsehead Nebula is difficult to observe visually but is a popular target for astrophotographers. NGC 2174 is a magnitude-6.8 emission nebula located about 6400 light-years from Earth. Messier 43 is a 9thmagnitude star-forming region about 1300 light-years away.



































