Fornax
Origin
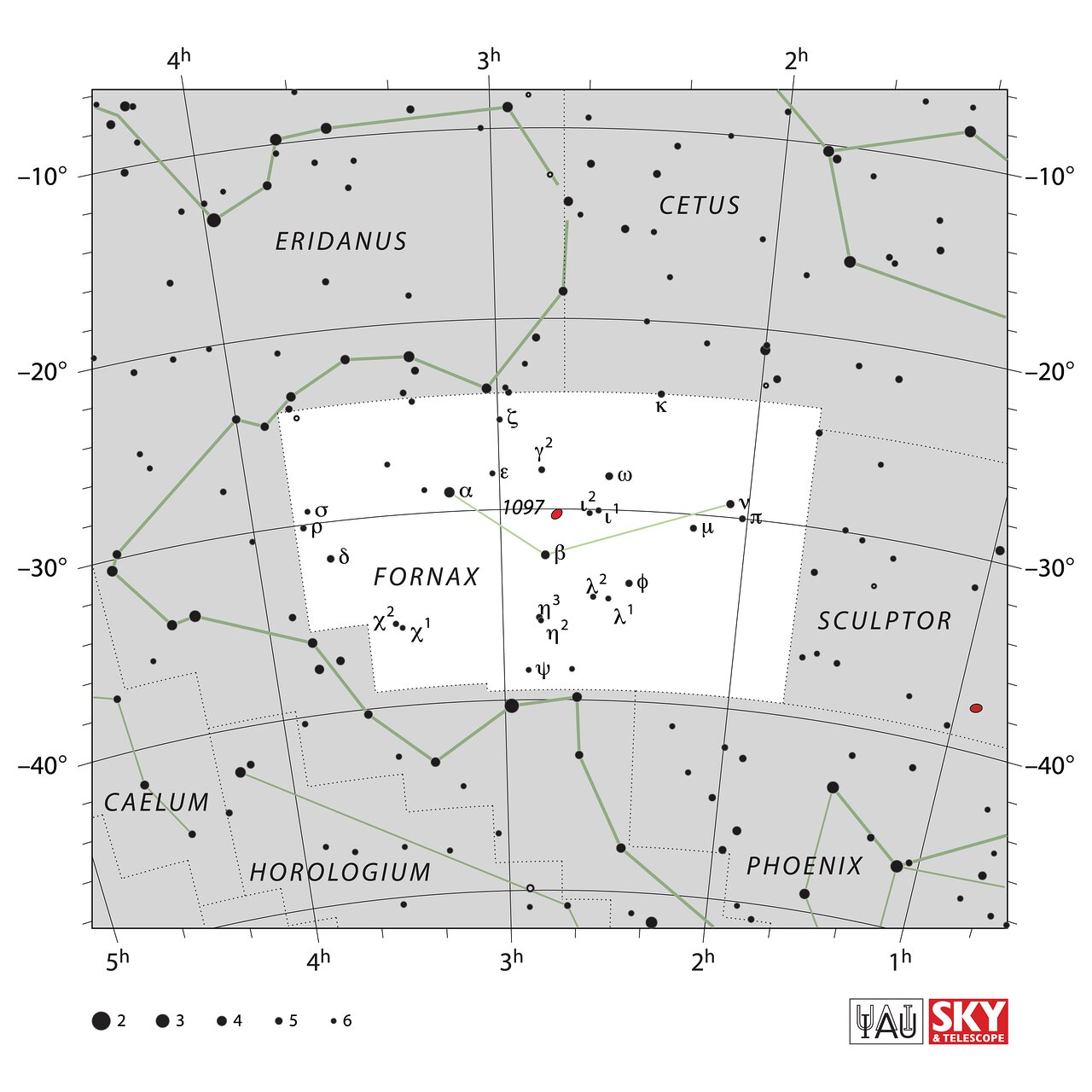
Fornax is a southern hemisphere constellation that represents a furnace. Fornax is partly circled by Eridanus. Fornax was named in 1756 by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille making it a modern constellation.
Bright Stars
Alpha Fornacis, or Dalim, is a double star system with a magnitude-3.91 yellow-white primary star and a magnitude-6.5 blue straggler located 46 light-years from Earth. Lacaille is a good target for amateur telescopes. Beta Fornacis is a yellow-white giant star shining at magnitude 4.5 and 178 light-years from Earth. Nu Fornacis is a blue giant shining at magnitude 4.7 and located 370 light-years away.
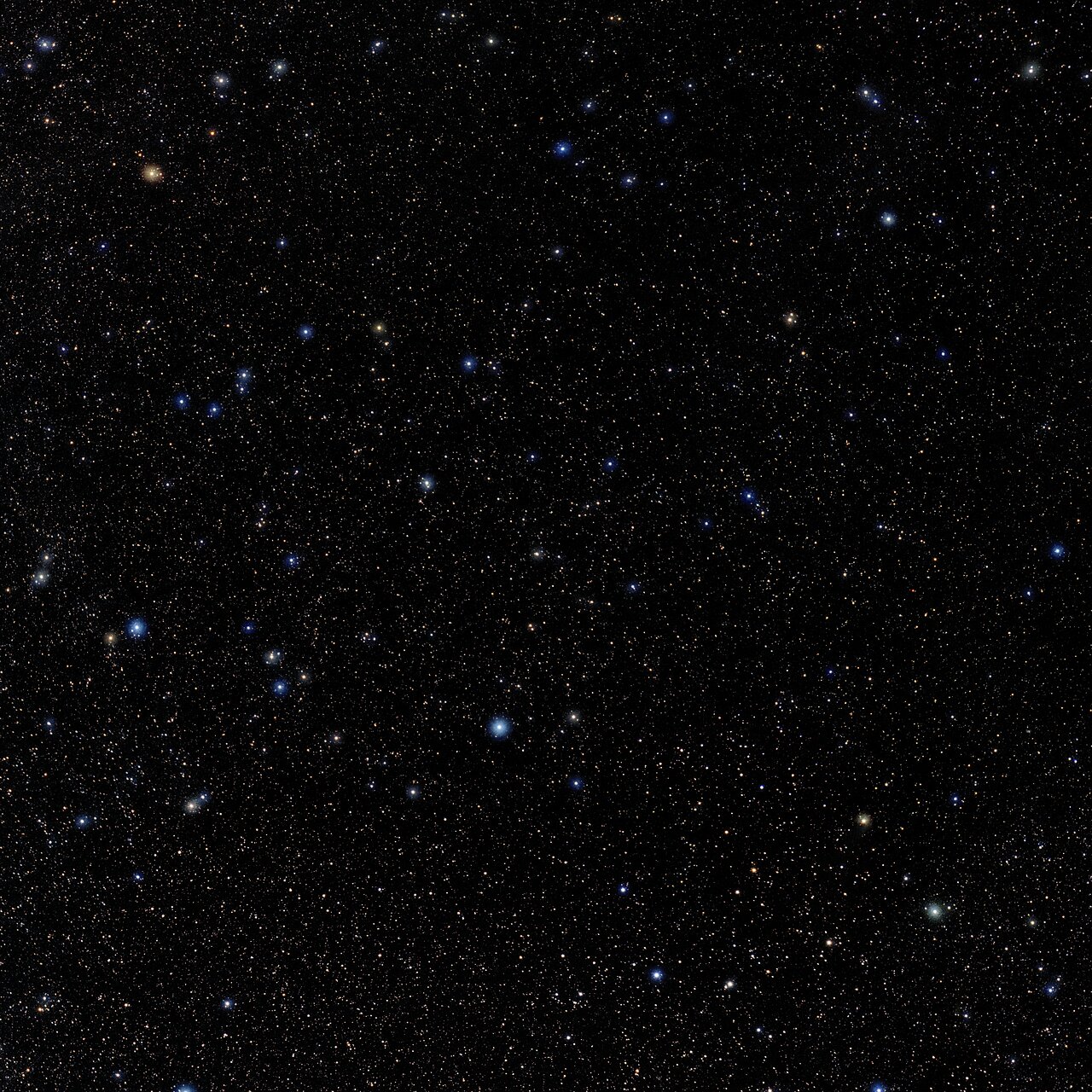
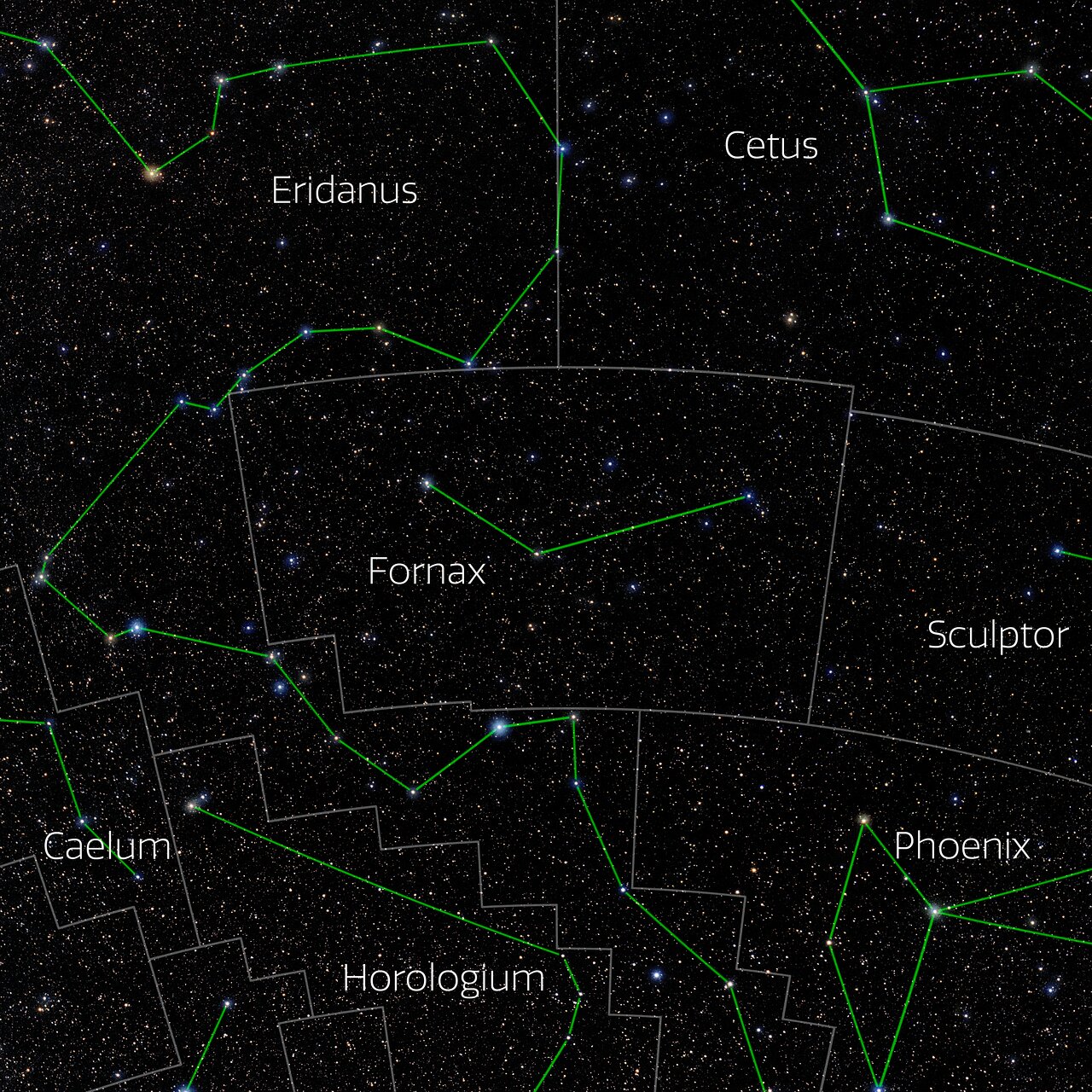

 Photo of the constellation Fornax produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Photo of the constellation Fornax produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Credit: E. Slawik/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani
Notable Objects
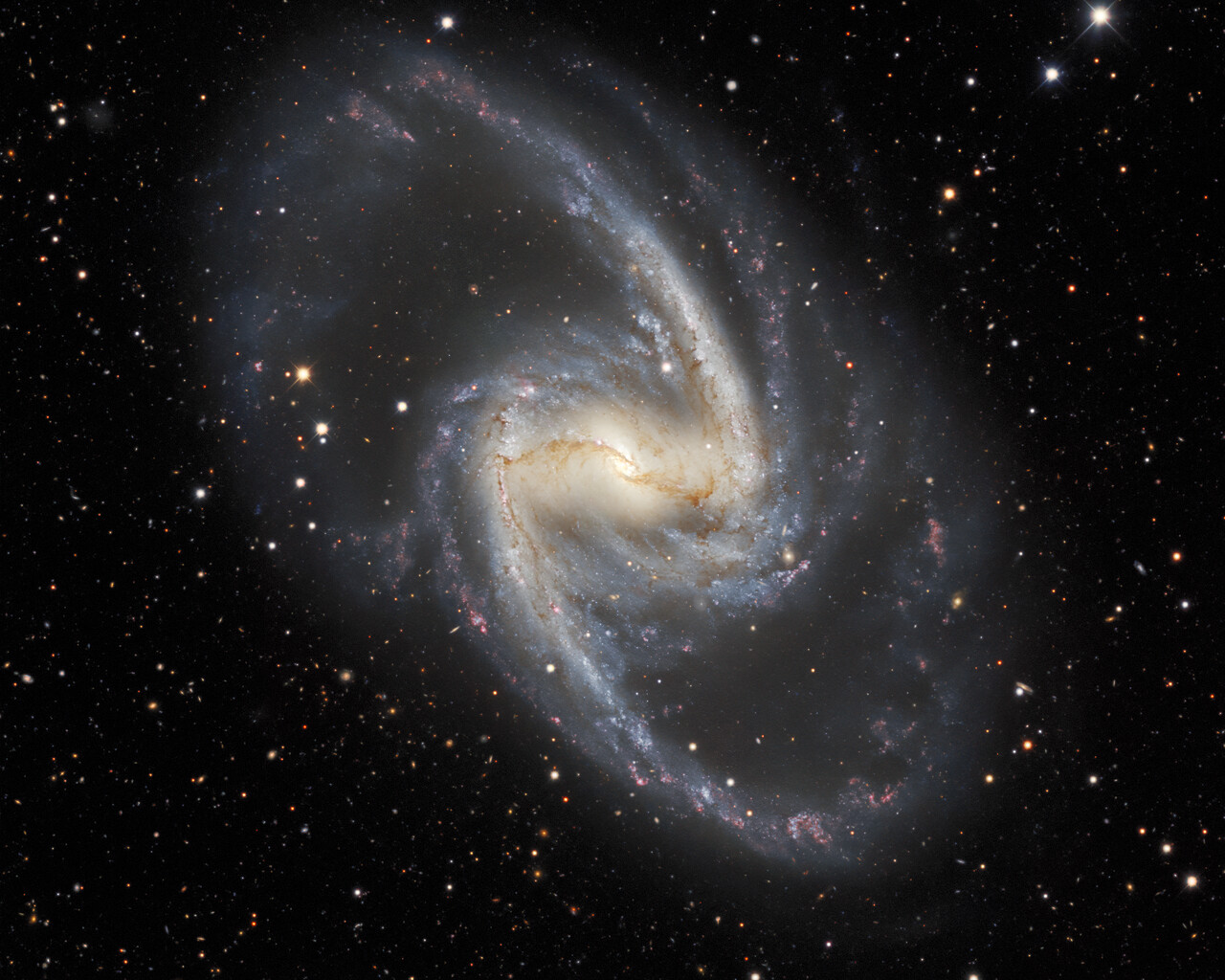
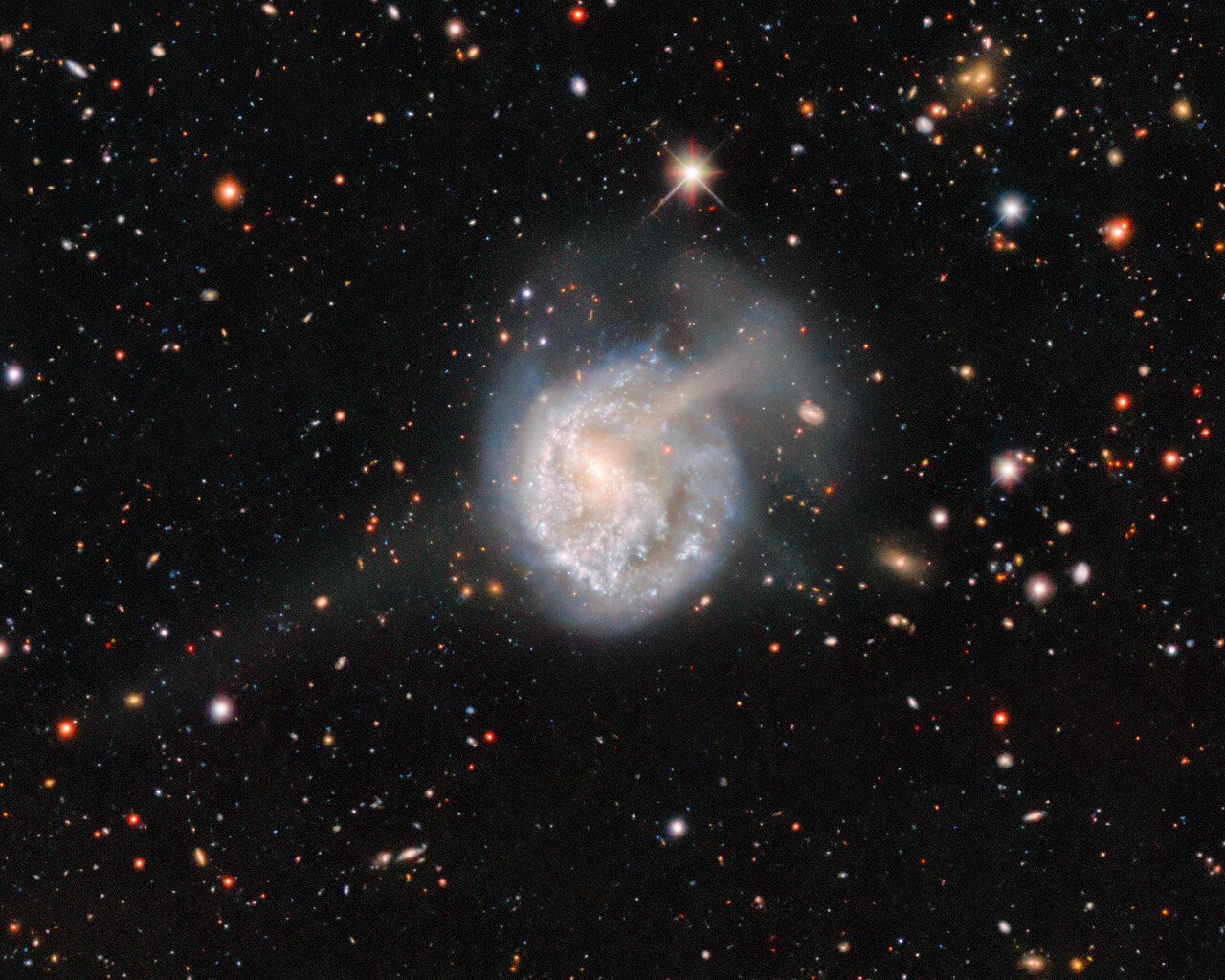
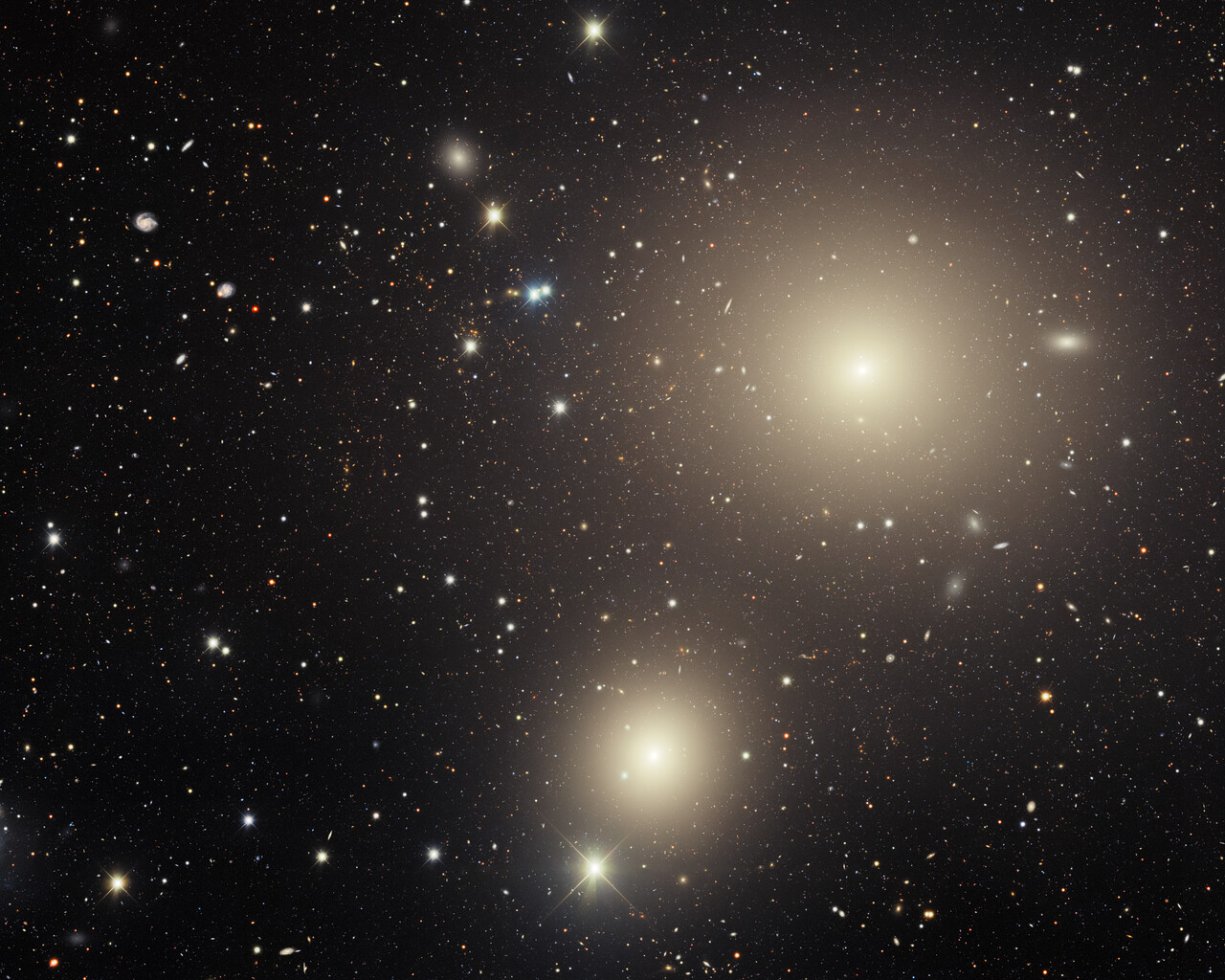
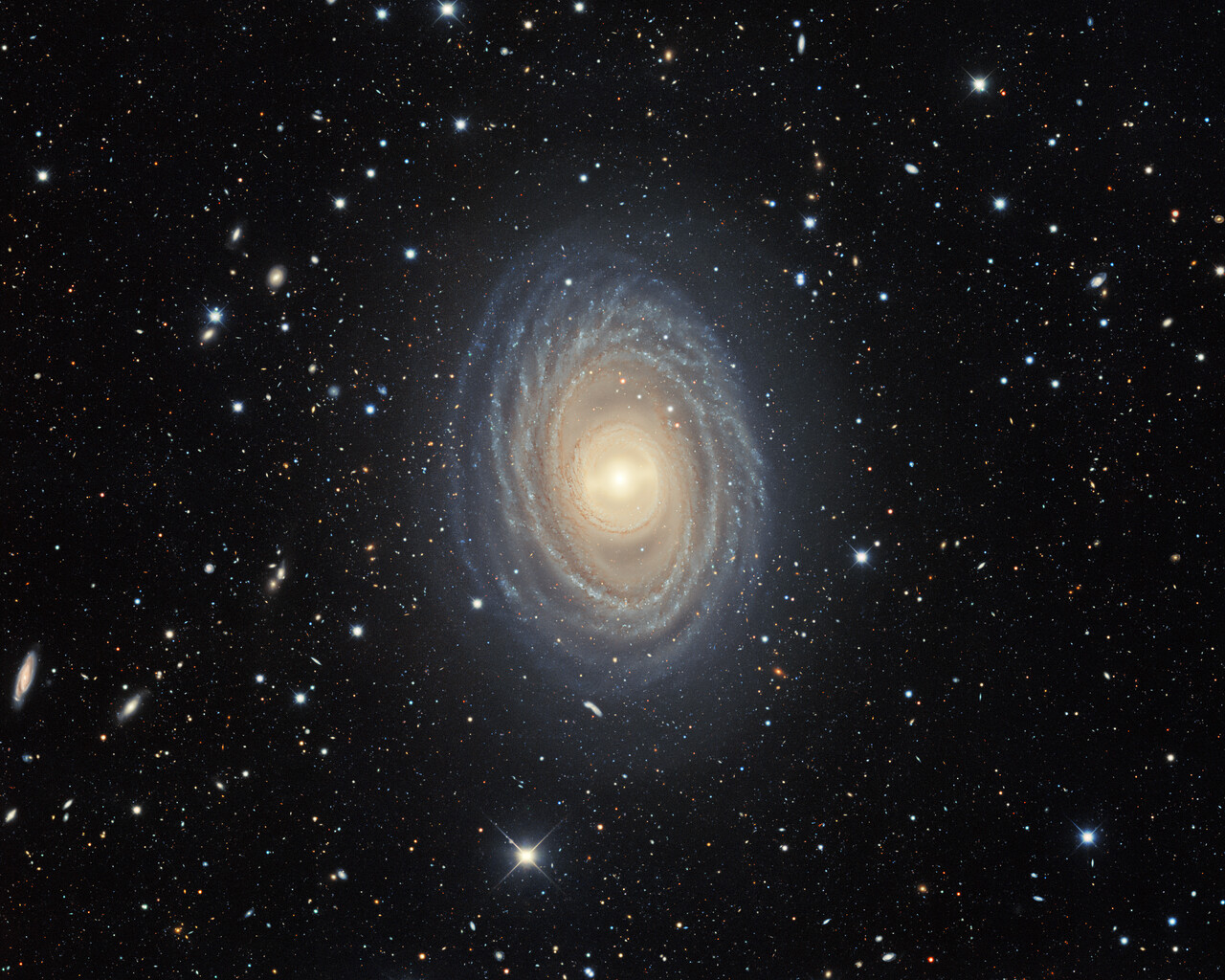
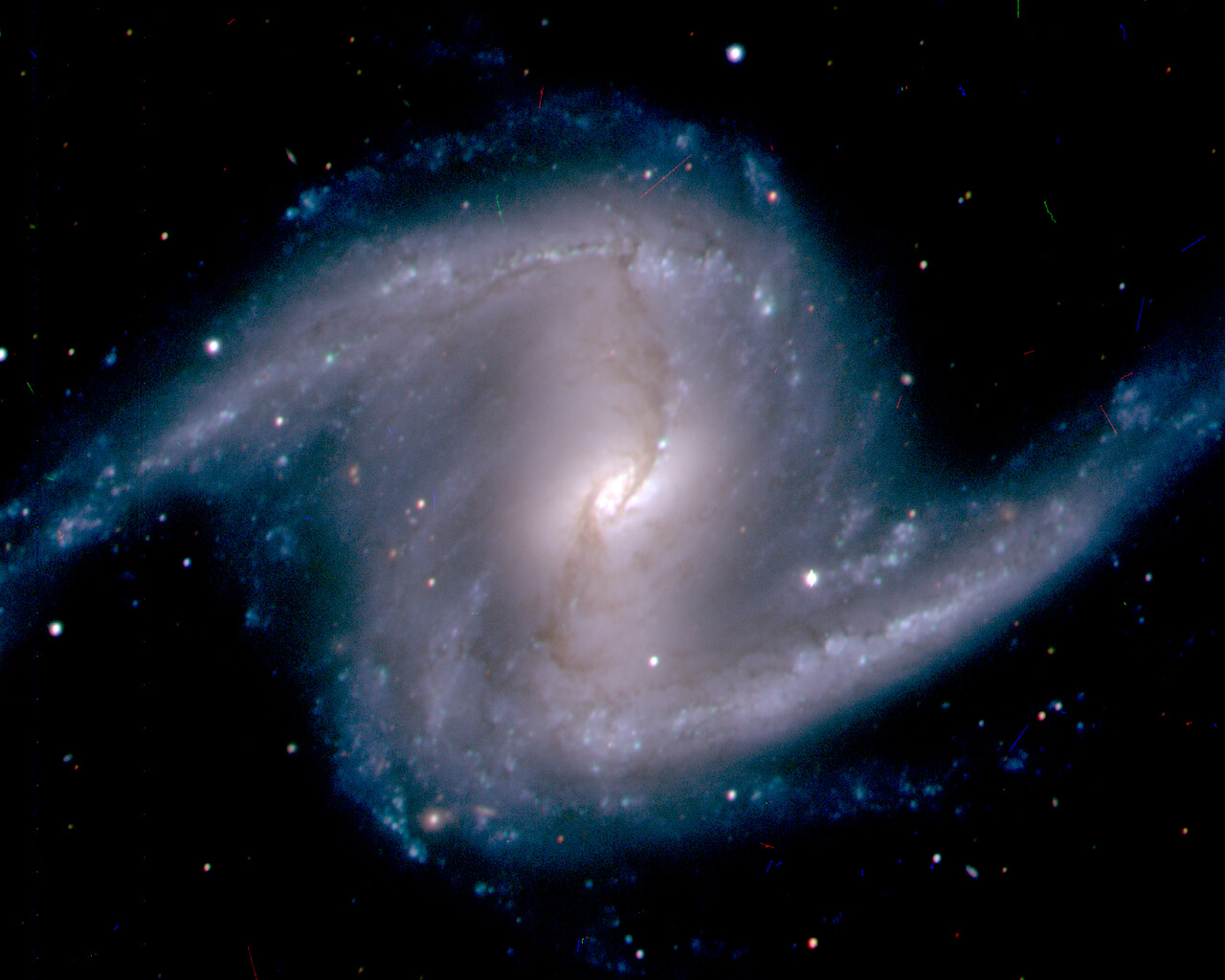
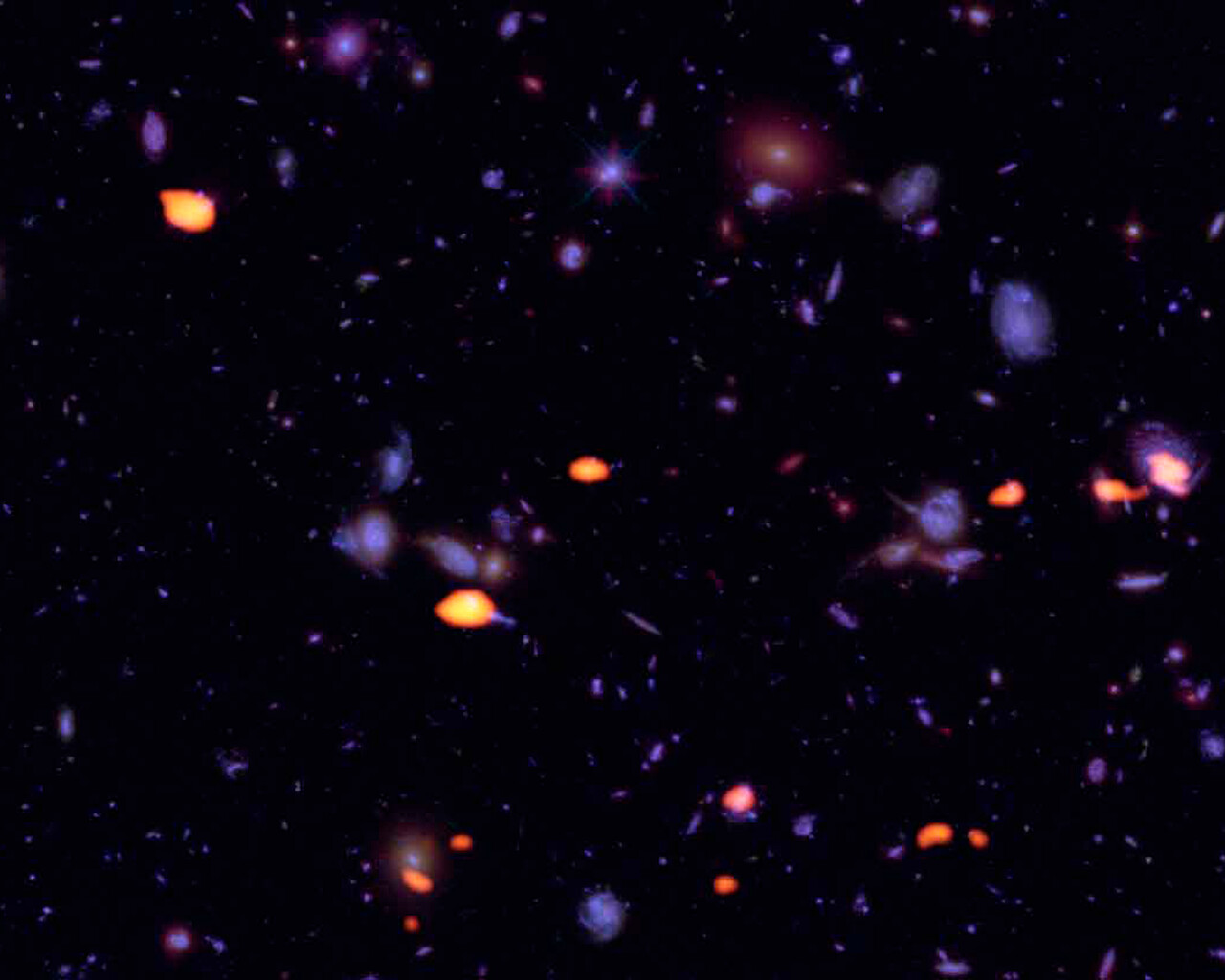
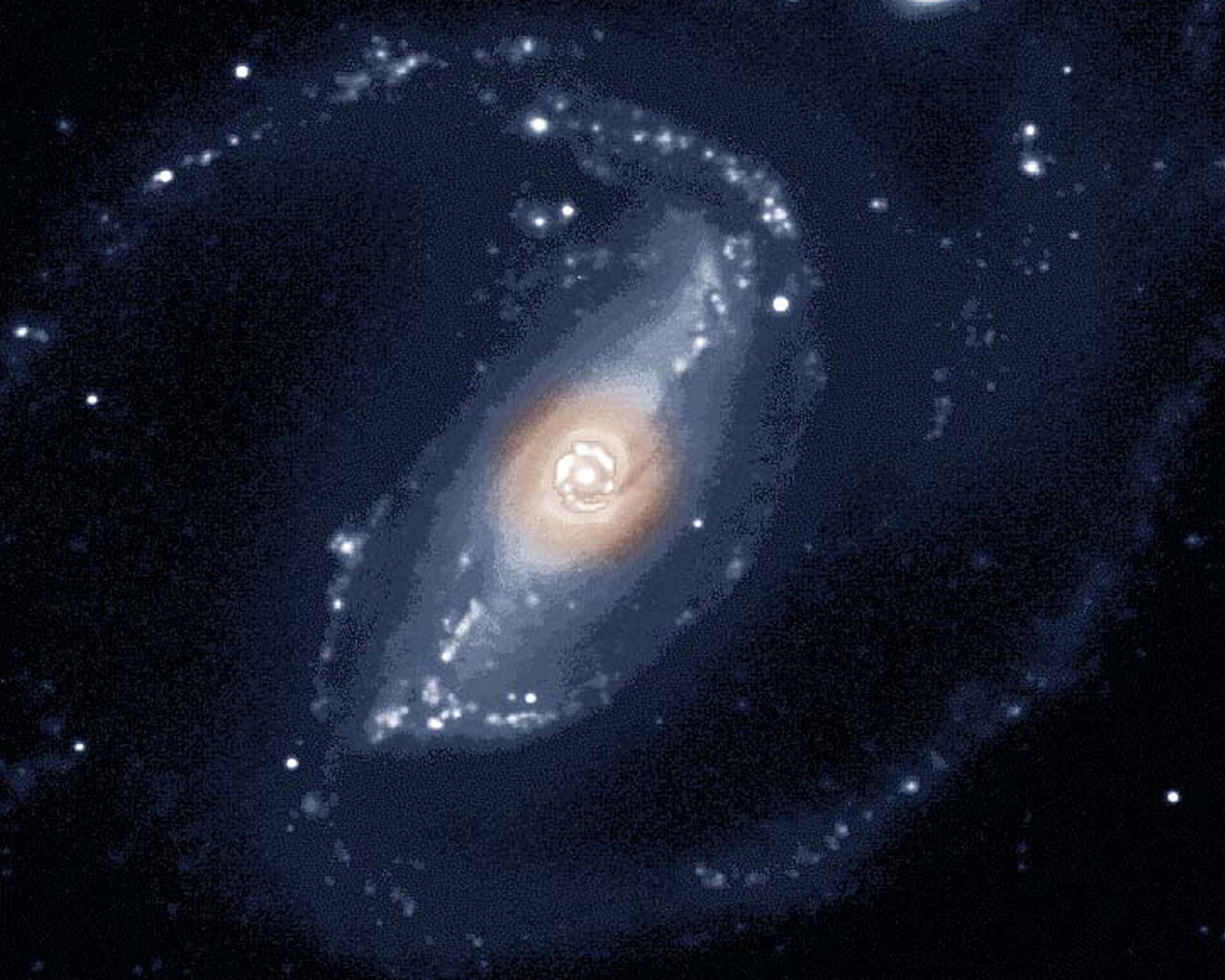
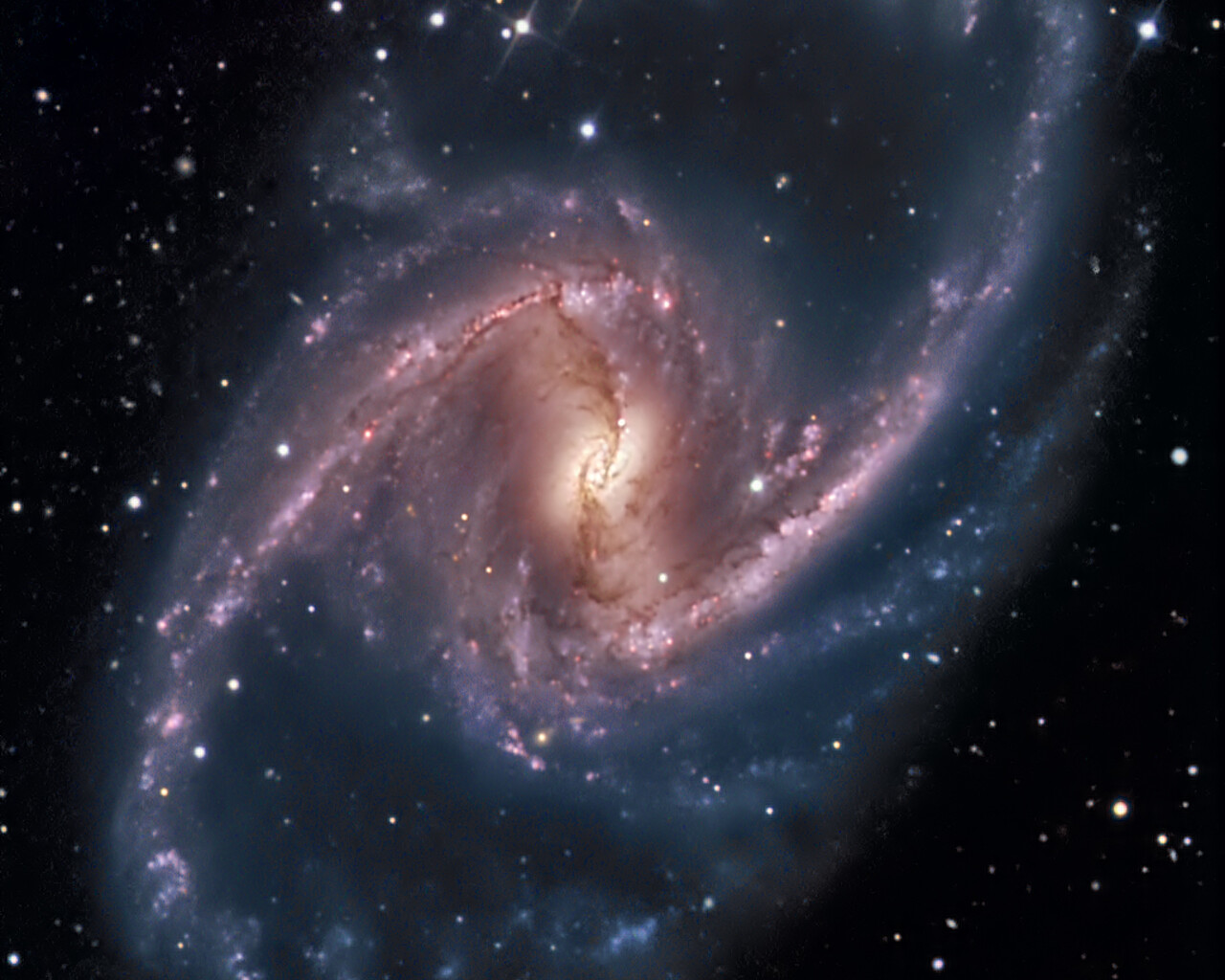
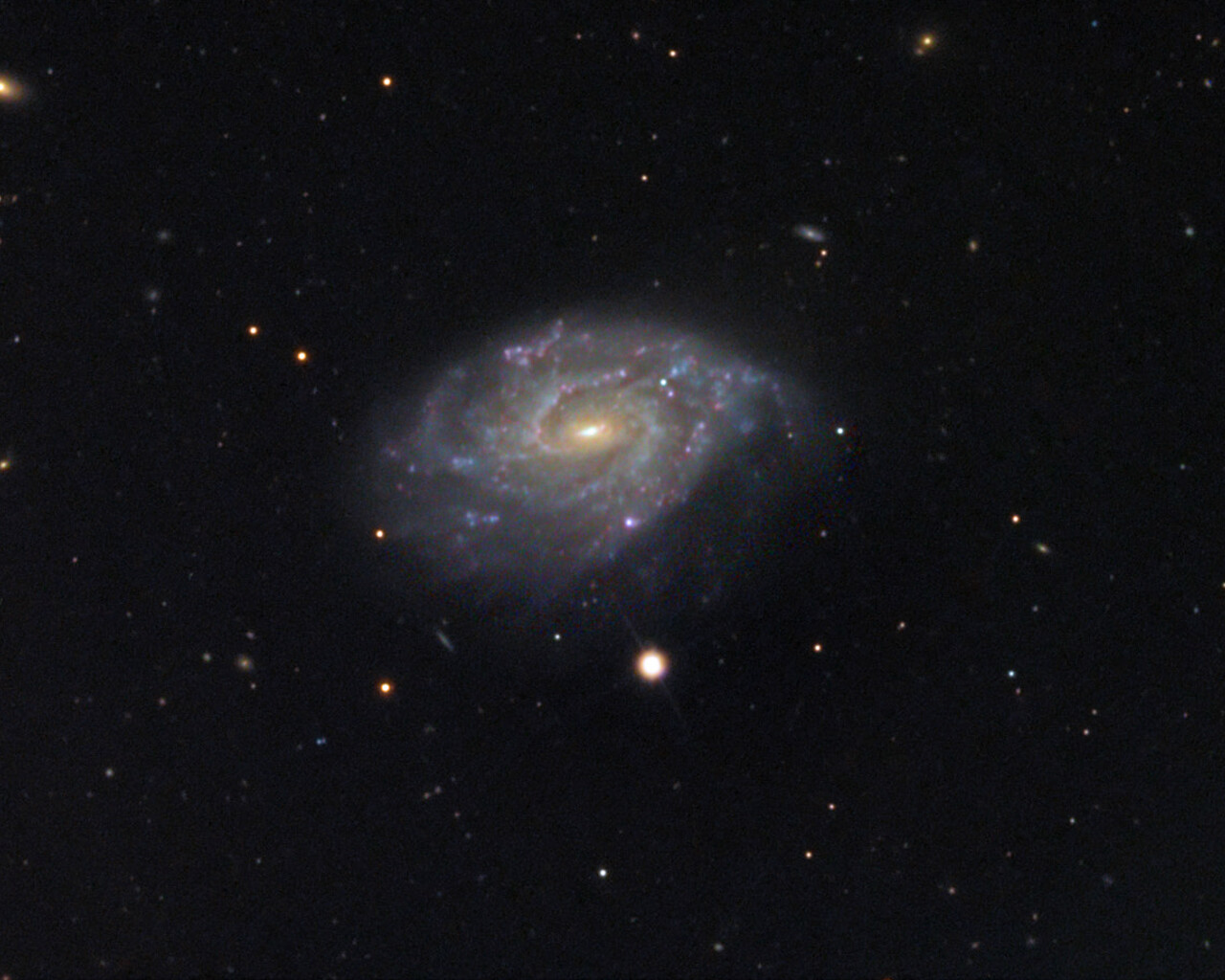
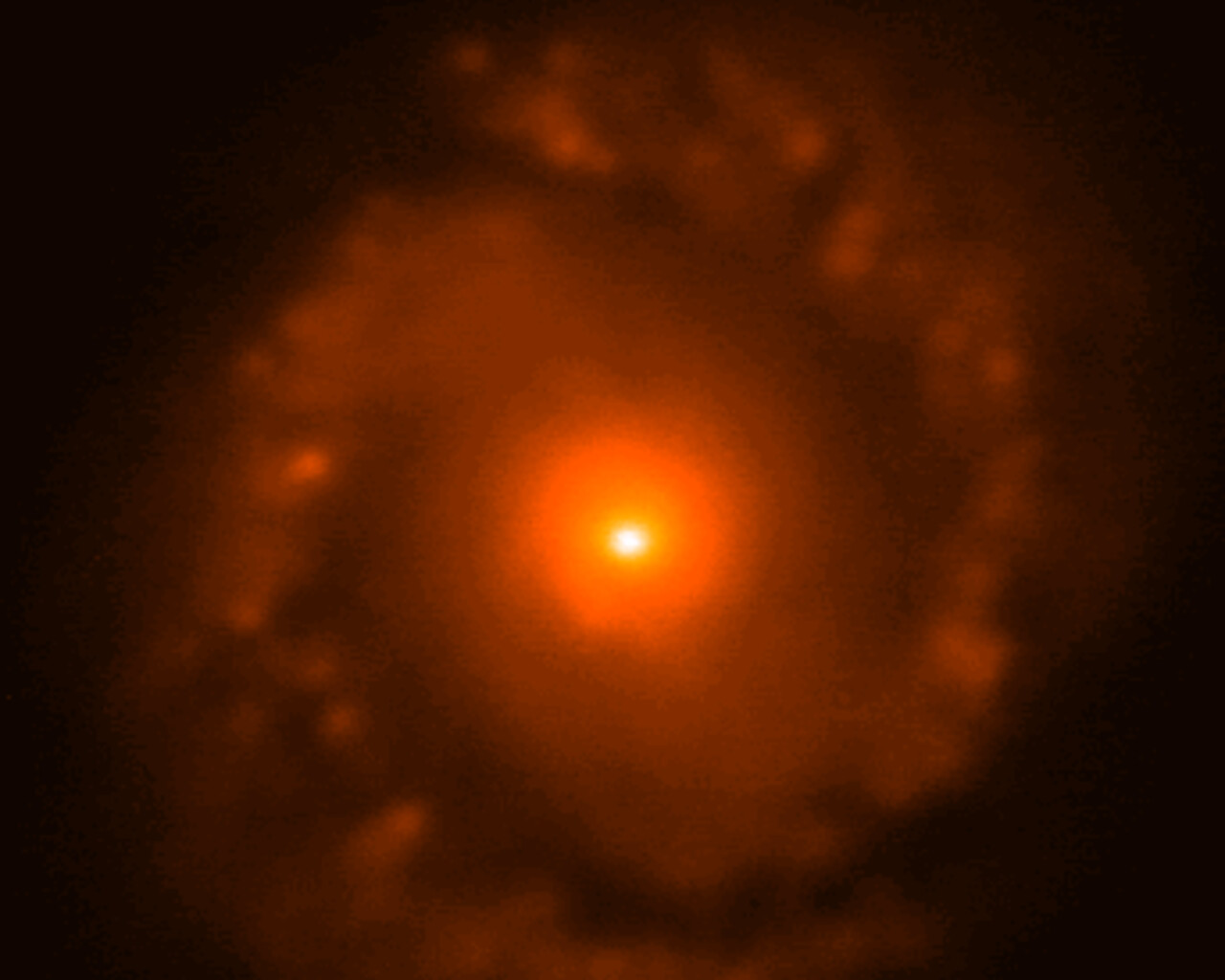
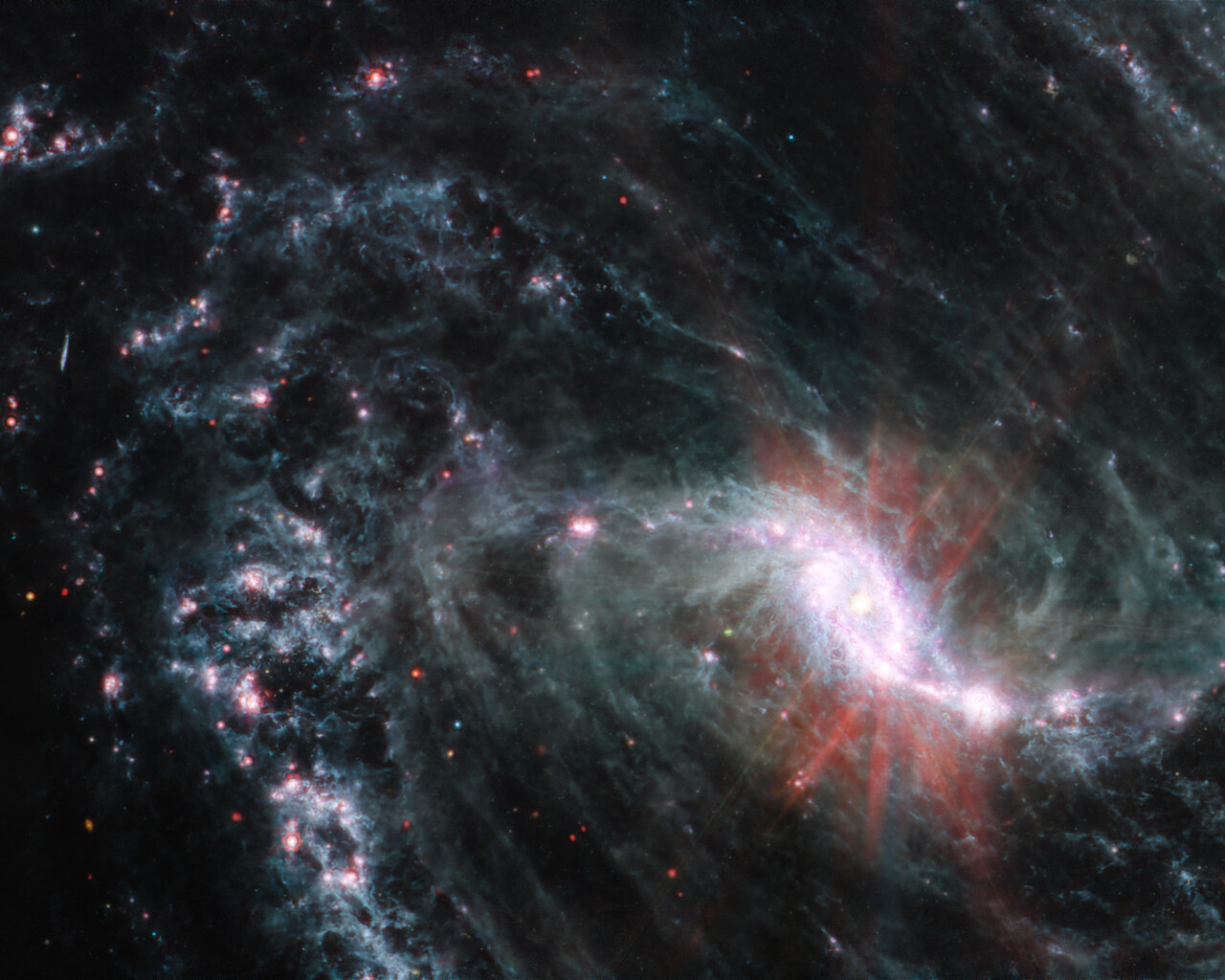
Fornax is home to the Fornax Dwarf Galaxy, a satellite of the Milky Way about 466,000 light-years away. The galaxy has a very low surface brightness, making it impossible to see visually. One of its globular clusters, NGC 1049, can be detected through larger amateur telescopes (10–12 inches and above). NGC 1360 is a 9th-magnitude planetary nebula in Fornax with an unusually bright 11th-magnitude central star. NGC 1097 is a 9th-magnitude barred spiral galaxy 45 million light-years away. Medium to large telescopes can explore the Fornax Galaxy Cluster located about 62 million light-years away.