Leo
Origin
Leo is among the easier constellations to identify, given the distinctive asterism shaped like a sickle, or a backwards question-mark, on its western side. The bright stars Regulus and Denebola mark the ends of the classical Greek constellation’s outline with the sickle on one end and a nearly perfect right triangle on the other. As a northern hemisphere constellation, Leo is best seen from northern latitudes, but is visible from the southern hemisphere as well, although not from extreme southern latitudes. Known as a springtime constellation, Leo is visible late at night during northern hemisphere winters (summers in the southern hemisphere), and visible in the early evening in the northern hemisphere spring (autumn in the southern hemisphere).
Bright Stars
Leo is easy to see even in moderately bright skies because of the large number of bright stars. Regulus (Alpha Leonis) shines at magnitude 1.34 and lies about 78 light-years from Earth. Denebola (Beta Leonis) shines at magnitude 2.23 and lies a mere 36 light-years away. Algieba (Gamma Leonis) is a binary star consisting of a magnitude-2.6 primary and a magnitude-3.6 secondary star 126 light-years from Earth. 40 Leonis lies nearby, giving it the appearance of a triple star system. Algieba is a pleasing sight in small telescopes. Zosma (Delta Leonis) is a magnitude-2.58 star 58 light-years from Earth.
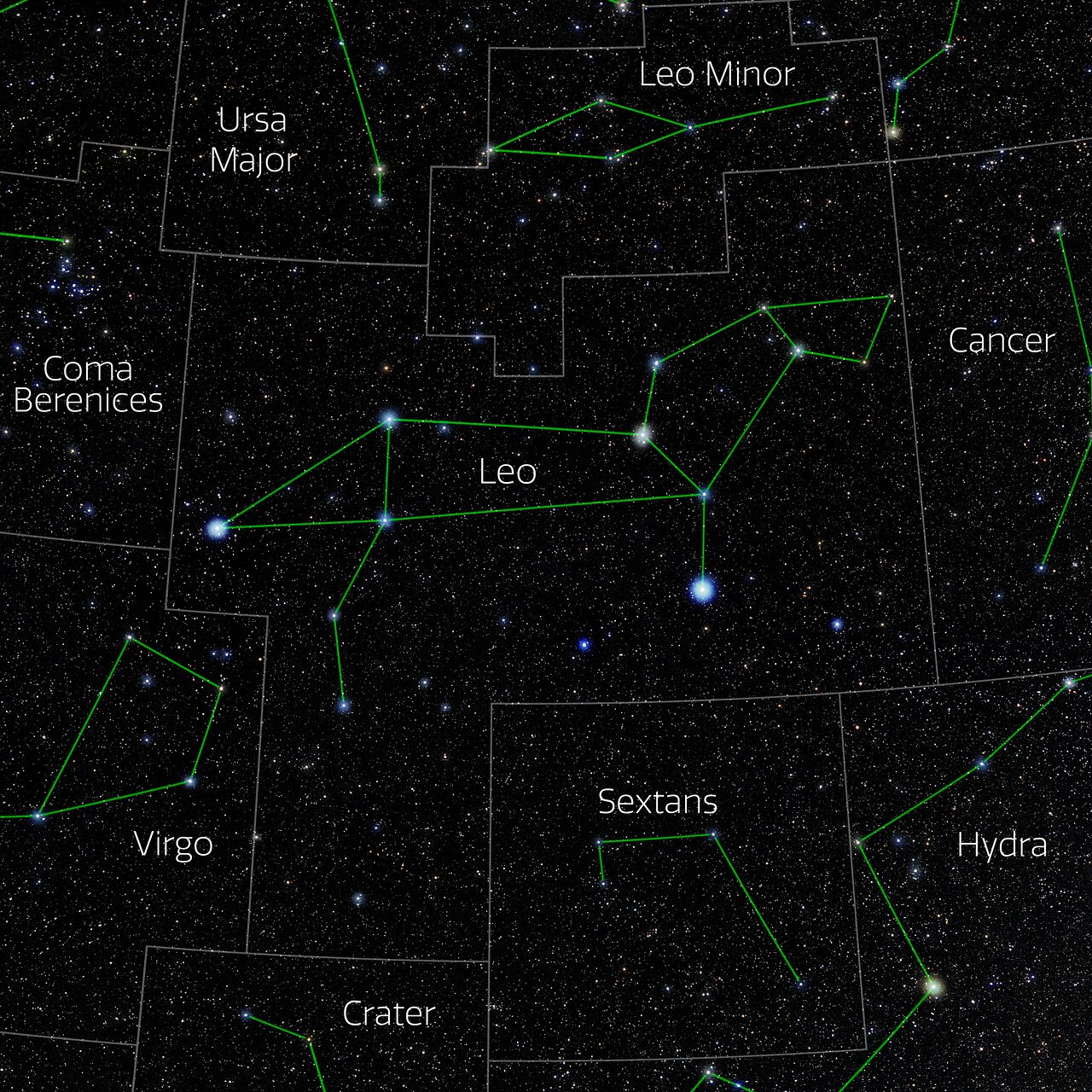

 Photo of the constellation Leo produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Photo of the constellation Leo produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Credit: E. Slawik/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani
Notable Objects
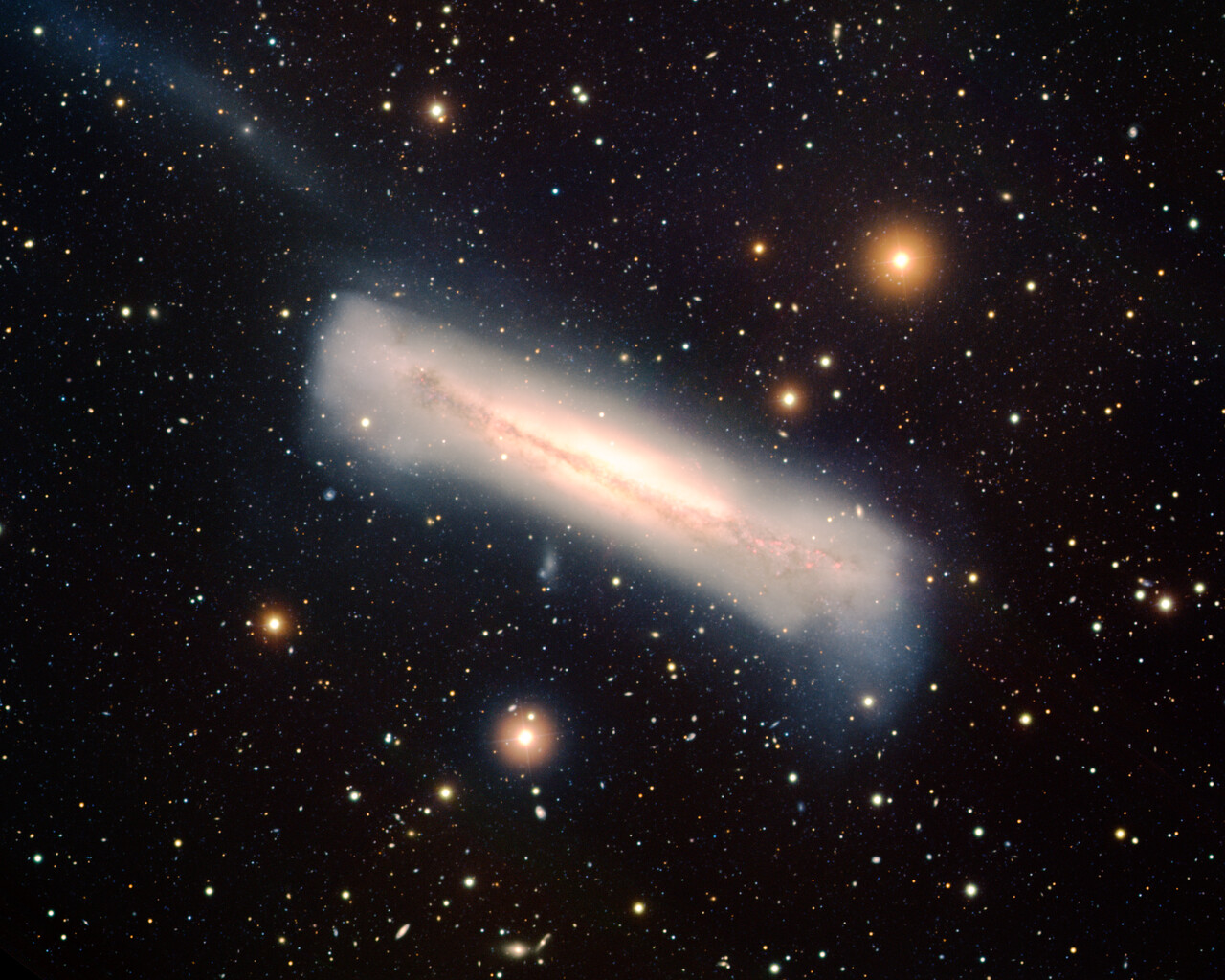
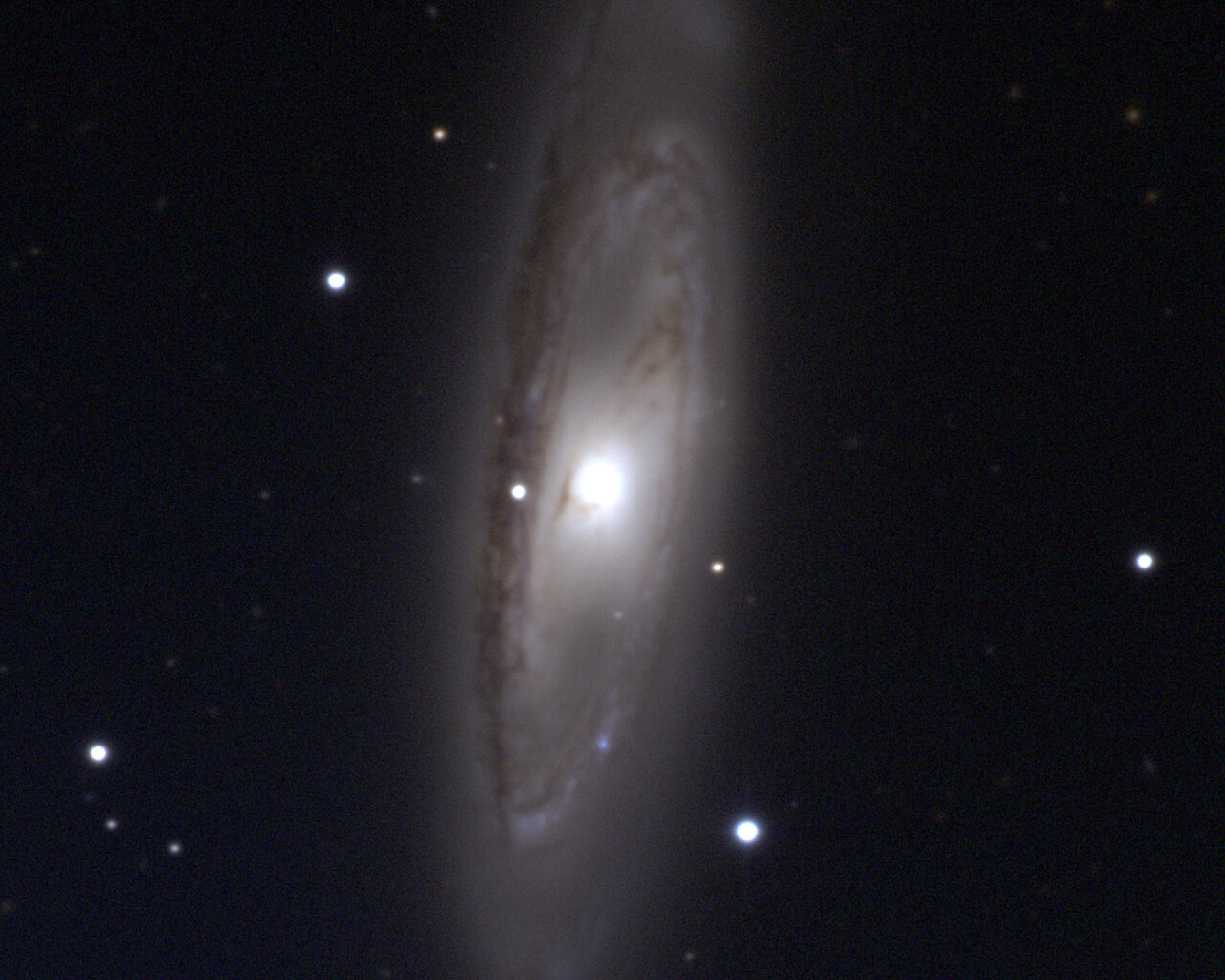
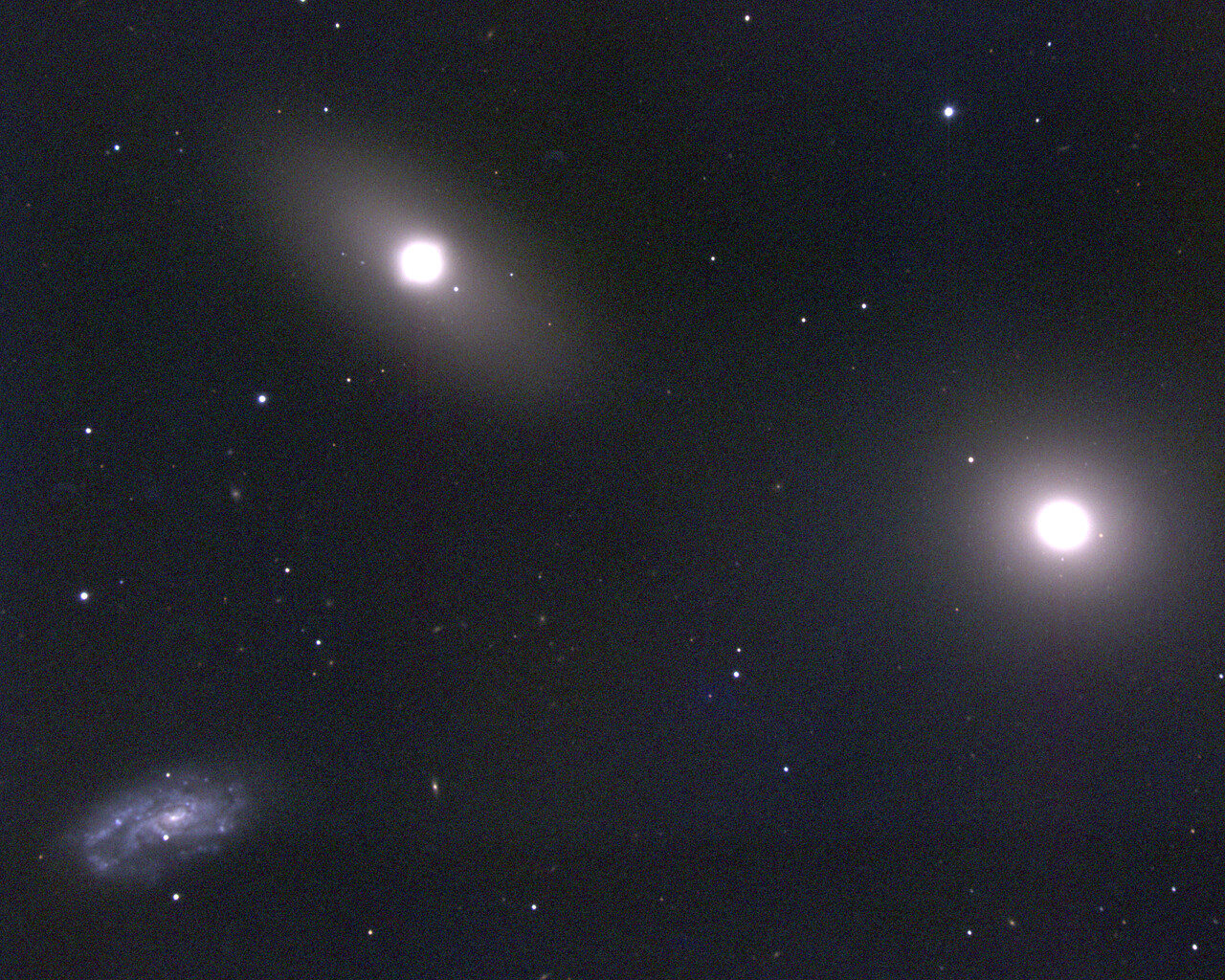
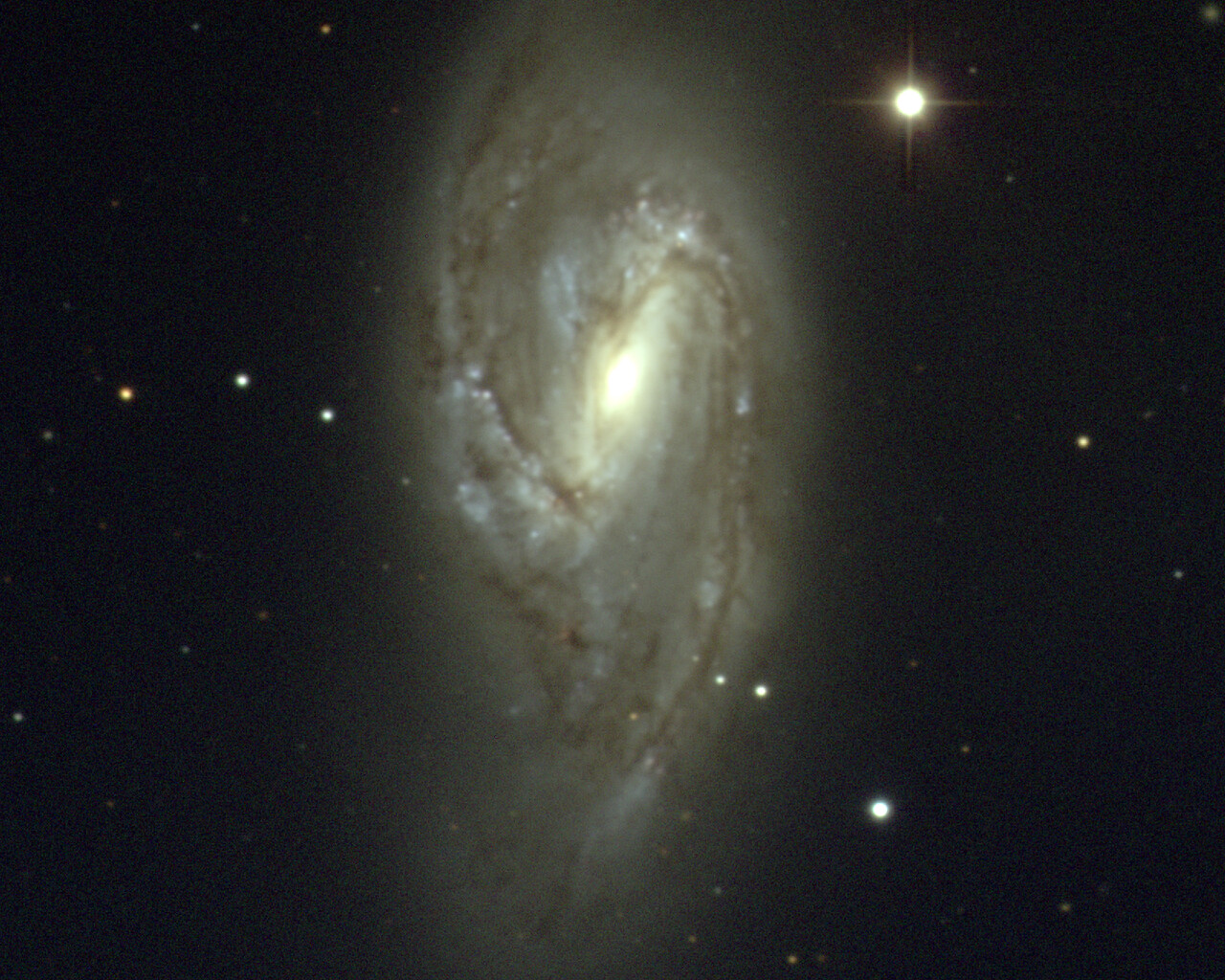
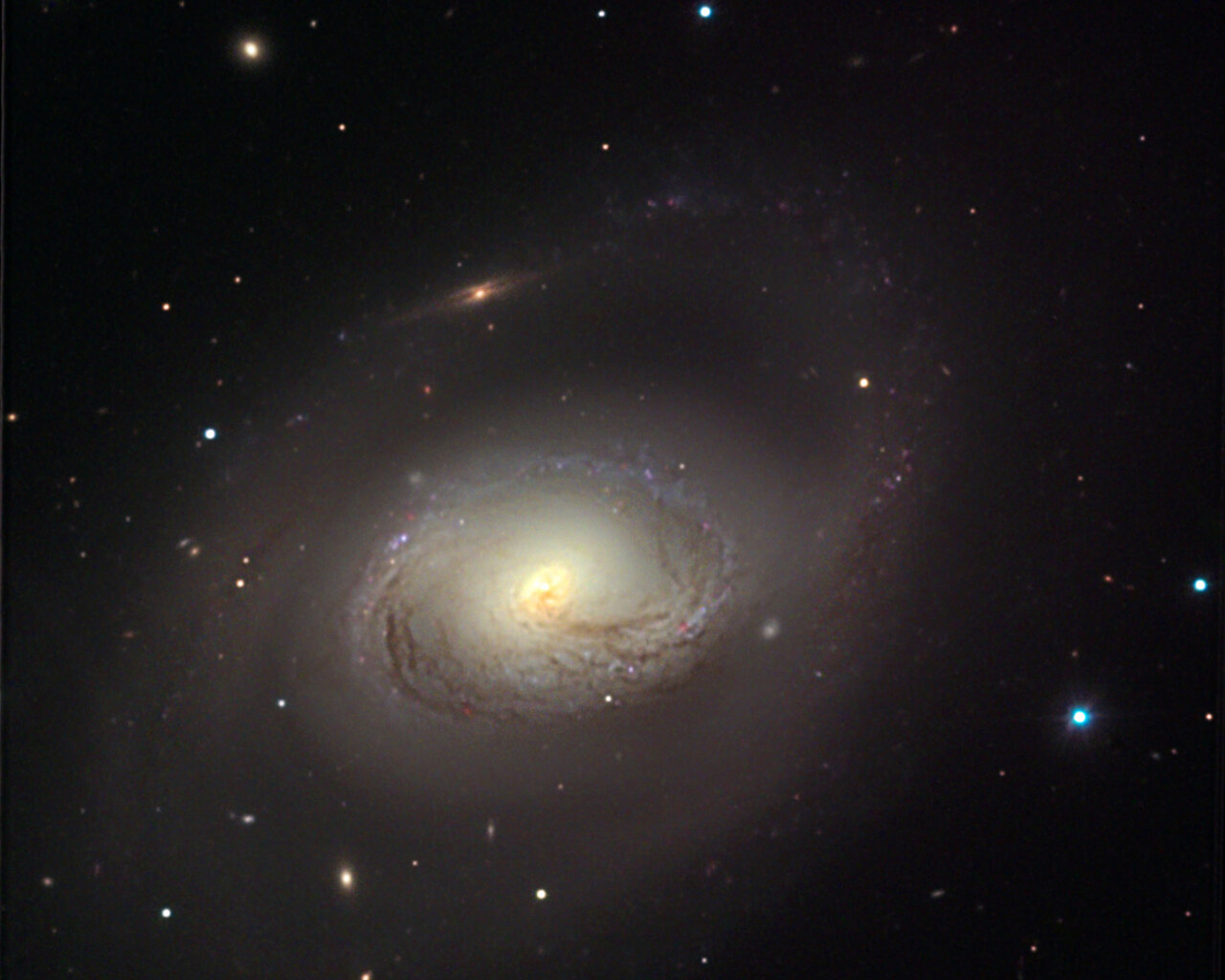
The most notable object is commonly known as the Leo Triplet and consists of three galaxies: Messier 65, Messier 66 and NGC 3628. These galaxies shine around 9th magnitude and are located 35 million light-years from Earth. They are visible in the same field of view in a small telescope. Messier 95 and Messier 96 are spiral galaxies located about 20 million light-years from Earth and separated by about 40 arcminutes, so they easily fit within the same field of view for a small telescope. M105 is a 9th-magnitude elliptical galaxy about a degree from the M95/M96 pair. NGC2903 is a 9th-magnitude barred spiral galaxy 25 million light-years away.























