Broader & Societal Impacts
Being a good steward of Earth and the sky is one of NOIRLab’s core principles. This commitment begins in our local host communities in Hawai‘i, Arizona and Chile with impacts that span our entire planet by shrinking the carbon footprint of our activities, preserving dark skies, and being good stewards of the lands that host our facilities (read more about NOIRLab’s societal impact in our communities in Chile, Arizona and Hawai‘i).
NOIRLab is committed to ensuring positive societal outcomes of our actions as a national center for ground-based astronomy. At the core of our activities is the concept of Broader Impacts, sometimes known as societal impact, which in our definition incorporates nine separate categories, seen above.
1. Workforce Development
|
To increase the science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) workforce, both inside and outside of NOIRLab, we take a multifaceted approach that combines attention to NOIRLab’s internal workplace culture, best practices in recruitment, and new professional development programs (mentorships, internships, fellowships, visitors). NOIRLab is committed to expanding quality opportunities and advancement opportunities for staff hired from our local host communities. NOIRLab partners with local universities and K-12 schools to promote awareness and develop skills in local workforces, and ~ 50% of our staff are from local workforces in our host communities. NOIRLab supports hundreds of highly skilled jobs in Chile, Arizona and Hawai‘i, 40–45 interns a year, and three prize fellows a year; hundreds of former NOIRLab staff — alumni — now work in astronomy, finance, management, communications, engineering, the aerospace industry, and related fields. NOIRLab also supports approximately 400 thesis projects and 550 non-thesis graduate students per year. |
 |
2. Local and Indigenous Engagement and Community Support
3. Education & Public Outreach
|
NOIRLab’s discoveries, facilities, technology, and people are featured in order to strengthen the public’s appreciation of science and the science community’s awareness of NOIRLab’s work. Educational programs increase the science-literacy of K–12 and college audiences, especially through data-driven materials. In a typical (pre-pandemic) year, NOIRLab reaches more than 100,000 followers on social media, and more than 5 million people in total Reach, and has more than 600,000 web visits. NOIRLab also leads or participates in more than 200 educational events a year with approximately 60,000 students and teachers. Over 750 photos, 40 of which are astronomical images, and 4 hours of ultra- and high-definition video, are published to the NOIRLab website. NOIRLab releases more than 60 web announcements, 30 press releases, 200 email newsletters, and 4700 social media posts each year. |
 |
4. Stewardship
5. Dark Skies Protection
| Since the introduction of urban illumination more than a century ago, the visibility of the pristine starry night sky has been gradually fading. Added to that, large constellations of communications satellites now being launched into Earth orbit are impacting on our ability to view and study the skies. NOIRLab’s efforts to limit light pollution and mitigate the impact of satellite constellations are vital if we are to ensure the sustainability of ground-based, nighttime astronomy and to preserve the natural night sky for everyone to appreciate. We work with partners to protect the night sky, while also supporting public benefits such as satellite-provided broadband connectivity to underserved regions. The work to preserve the dark night sky has broader impacts as light pollution not only negatively impacts our ability to study the Universe, but also has negative effects on energy consumption, our health and that of wildlife and ecosystems. |  |
|
NOIRLab’s Globe At Night Citizen Science program has recorded more than 250,000 measurements of night sky brightness from the public since 2006. NOIRLab has assisted communities in Arizona, Hawai‘i, and Chile to establish several official ordinances to control artificial light pollution, and organized four key conferences with satellite operators and manufacturers and dark skies experts. Since early 2022 NOIRLab is co-hosting the IAU Centre for the Protection of the Dark and Quiet Sky from Satellite Constellation Interference. Key NOIRLab staff have also played leading roles in IAU’s Site Protection Commissions for over 45 years and the International Dark Sky Association for over 20 years. Read more about NOIRLab’s Dark Skies Protection efforts here. |
|
6. National and International Collaboration
|
NOIRLab Programs foster and rely on international and national partnerships, including the US Department of Energy, NASA, and university groups. NOIRLab is a proponent of open data and standards in astronomy and is committed to several collaborations including contributing toward protecting Earth from asteroid threats, being a role model for partnerships in Research & Development, promoting national and international partnerships, mitigating satellite constellation side-effects, leading ground-based optical astronomical research, and fostering local scientific development in all three of our host communities and regions. |
 |
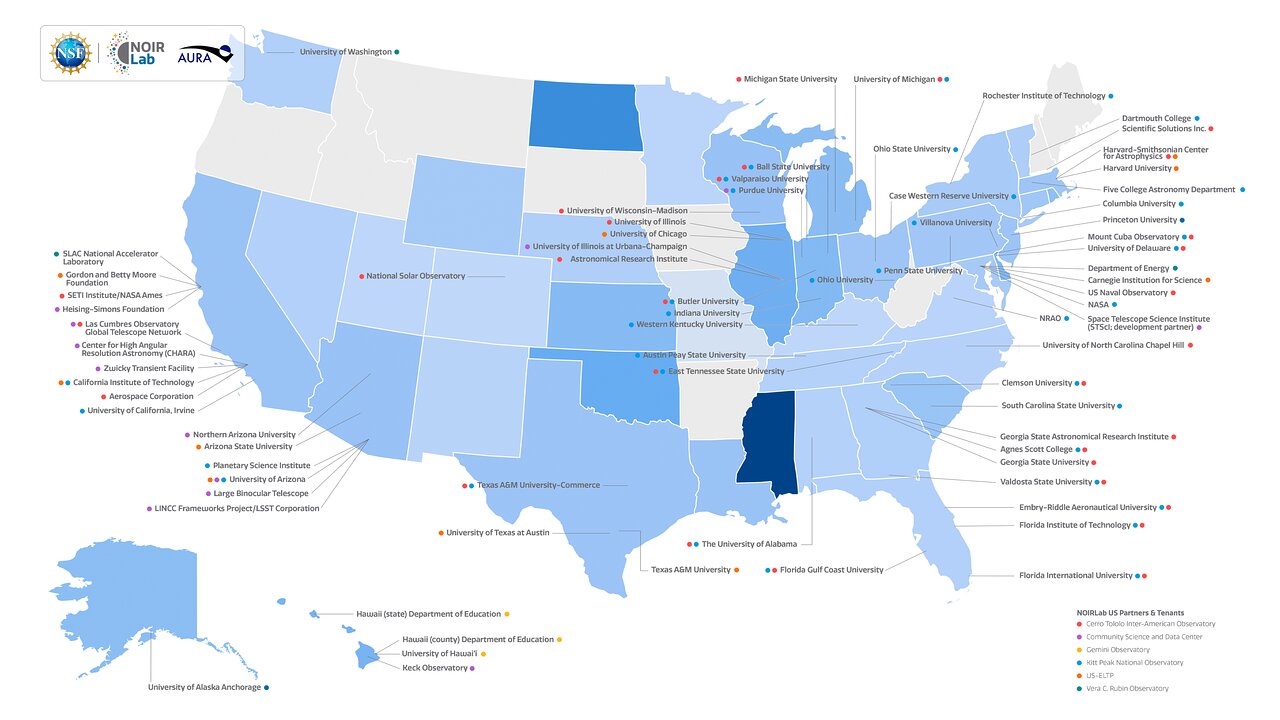
US Partners and Tenants* |
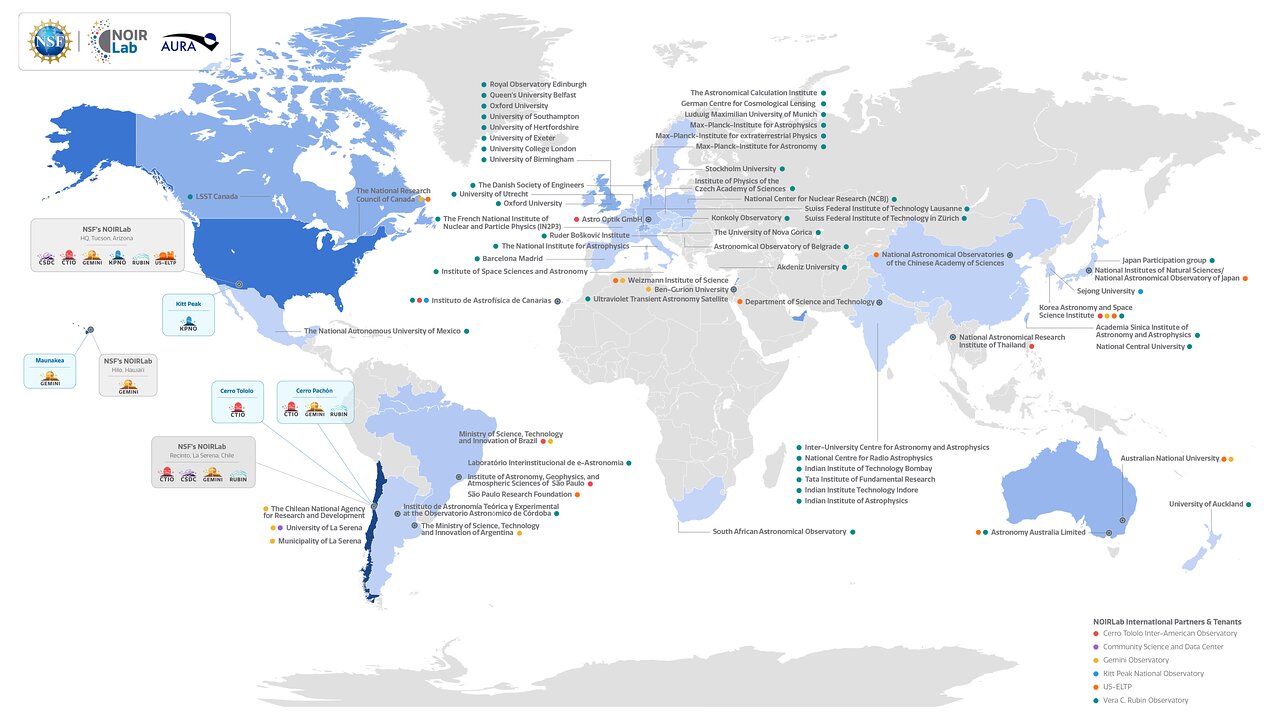
International Partners and Tenants* |
|
*maps do not display all the Instrumentation Partners we collaborate with |
|
7. Technology Innovation & Industry
8. Research
|
Research is a foundational pillar for society and NOIRLab. Science is one of humankind’s greatest collective endeavors and advances our knowledge of how the Universe works. It is a discipline that opens our eyes, that gives context to our place in the Universe and that is able to reshape how we see the world. Although “blue-skies research” like astronomy rarely leads directly to tangible outcomes on a short timescale, the pursuit of this research requires cutting-edge technology and methods that can, on a longer time scale, make a difference through their broader application. The fruits of scientific and technological development in astronomy, especially in areas such as optics and electronics, have become essential to our day-to-day life, with applications such as personal computers, communication satellites, mobile phones, Global Positioning Systems, solar panels and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners. |
 |
|
Although the study of astronomy has provided a wealth of tangible, monetary and technological gains, perhaps the most important aspect of astronomy is not one of economical measure. It inspires us and promises answers to the big questions. It acts as a window onto the immense size and complexity of space, putting Earth into perspective and promoting global citizenship and pride in our home planet. On a yearly basis, NOIRLab research generates data for more than 700 scientific peer-reviewed papers, 400 of which use more than one NOIRLab telescope or facility. NOIRLab staff author or co-author more than 300 papers a year. Currently NOIRLab’s research data holdings constitute more than 7.3 petabytes of data, 13.5 million observations, and 80 billion individual measurements of stars and galaxies. More than 1000 proposals for research are received per year by NOIRLab, and both the 2011 “Dark Energy” (see this press release and web announcement), and the 2020 “Milky Way supermassive black hole” (see this press release and web announcement) Nobel Prizes in Physics used NOIRLab data to help achieve their findings. NOIRLab is strengthening its user community communications to provide timely and accurate information of relevance to the scientific users of our facilities and data, and to have two-way conversations about the needs of our user community. Effective communication through the science website, social networks, scientific conferences, print and electronic publications is establishing a reliable flow of scientific, programmatic, operational, and proposal-relevant information. Community engagement is critical for the US ELT Program’s Key Science Programs. |
|