Perseus
Origin
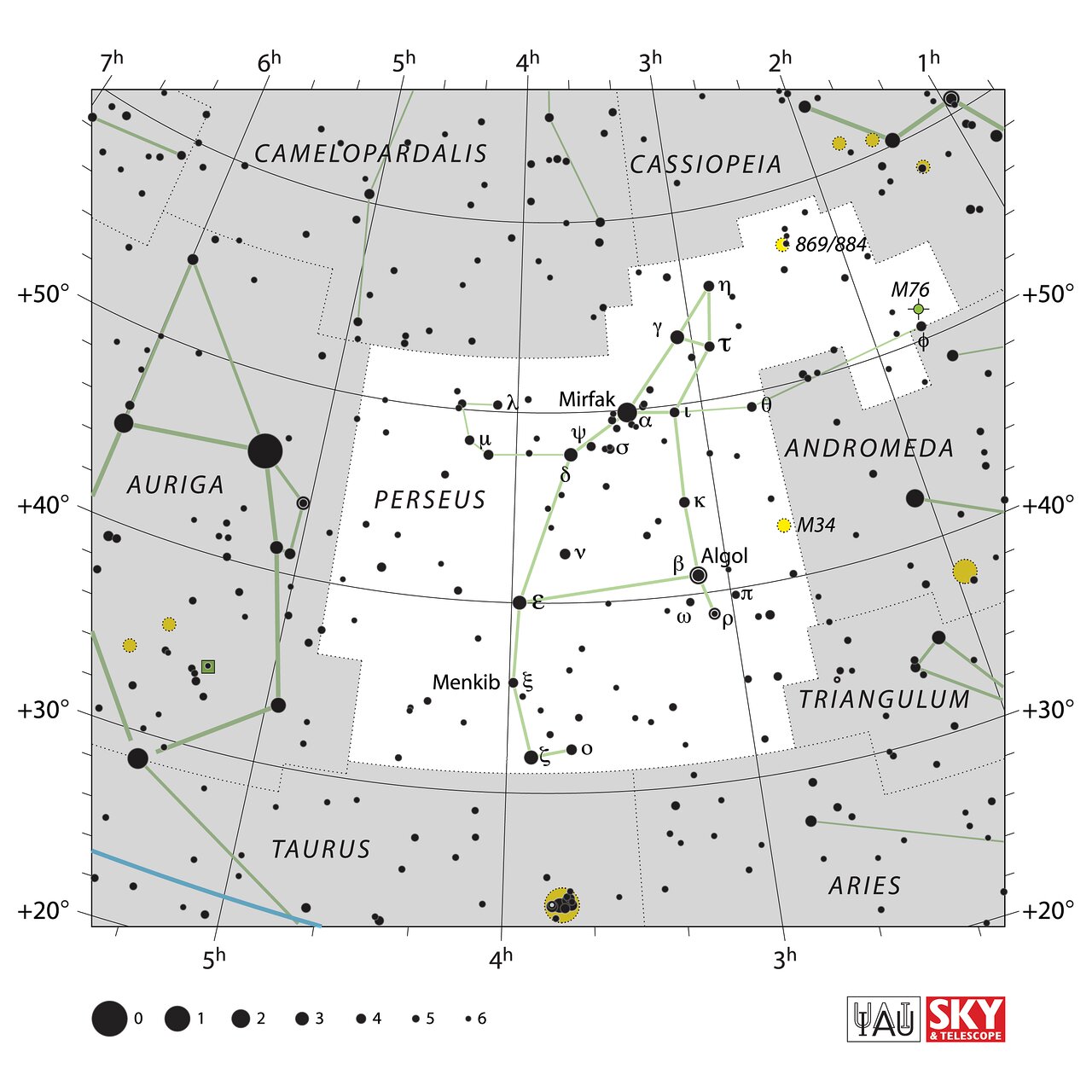
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy and is among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north.
Bright Stars
Algol is a variable star with an apparent magnitude that varies from a minimum of 3.5 to a maximum of 2.3 over a period of 2.867 days.
AG Persei is another Algol variable in Perseus, whose primary component is a B-type main sequence star with an apparent magnitude of 6.69.
Mirfak, or Alpha Persei is the brightest star of this constellation with an apparent magnitude of 1.79.
Zeta Persei is the third-brightest star in the constellation at magnitude 2.86.


 Photo of the constellation Perseus produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Photo of the constellation Perseus produced by NOIRLab in collaboration with Eckhard Slawik, a German astrophotographer.
The annotations are from a standardized set of 88 western IAU constellations and stick figures from Sky & Telescope. Please find here a non-annotated version of the image.
Credit: E. Slawik/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/M. Zamani
Notable Objects
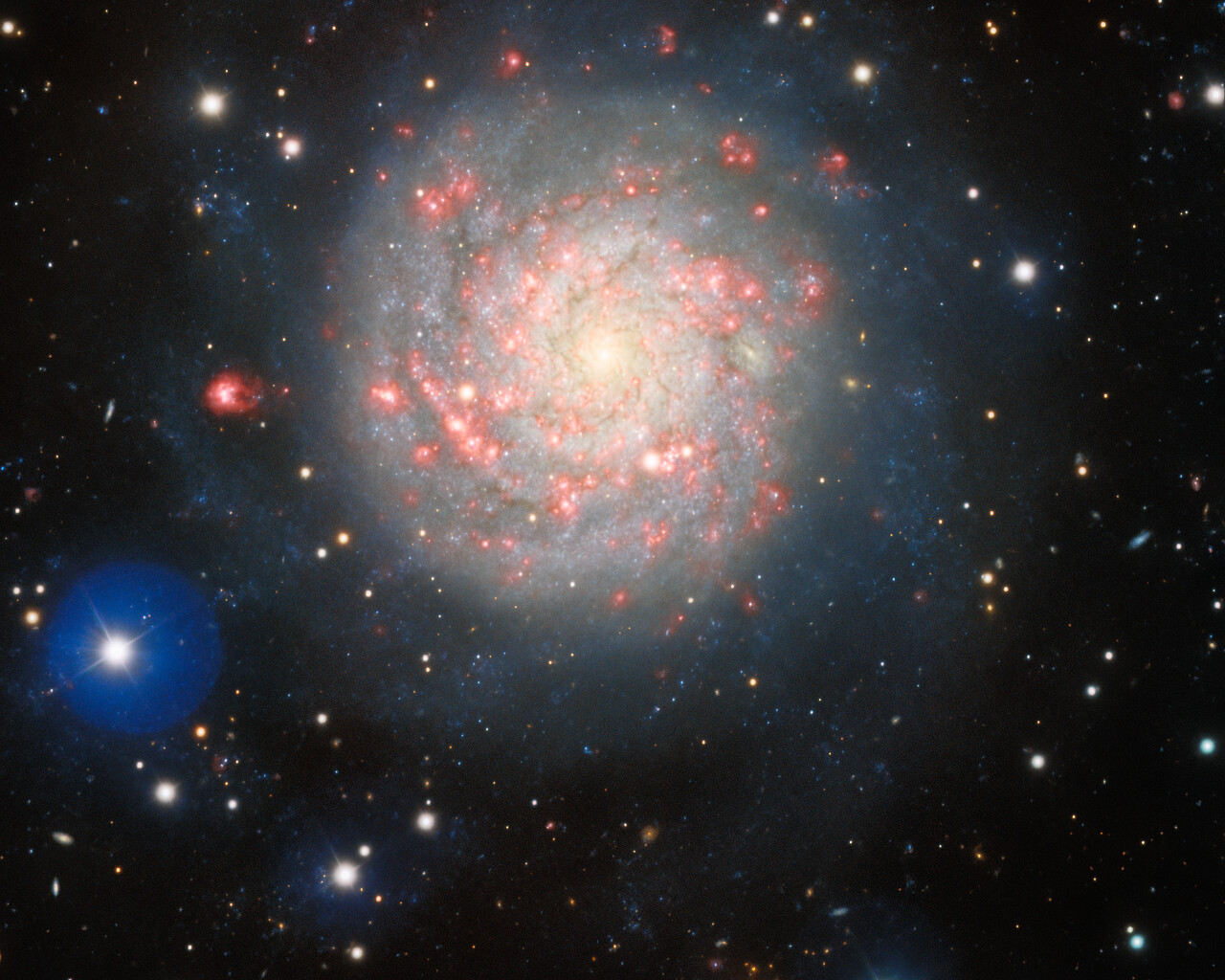
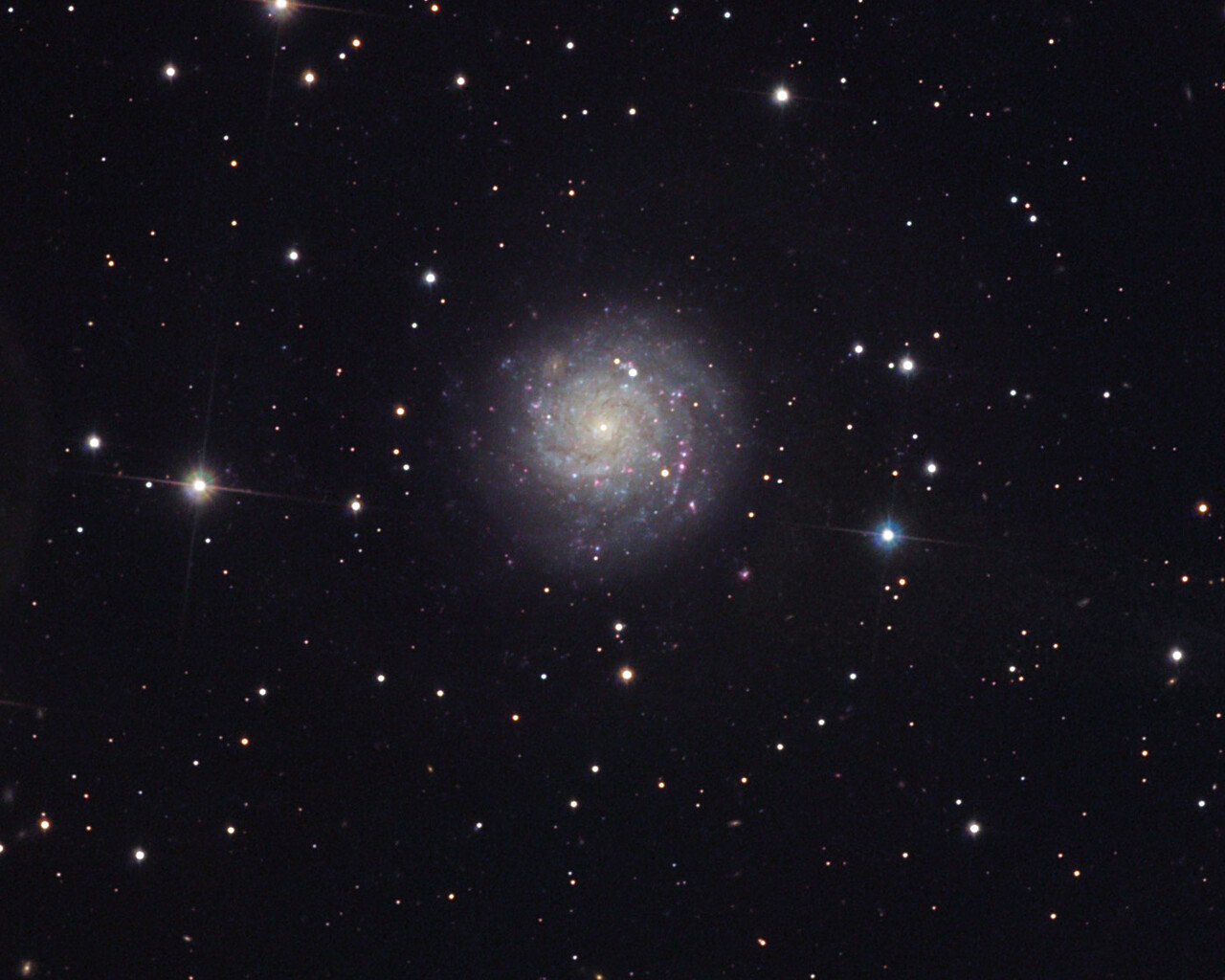
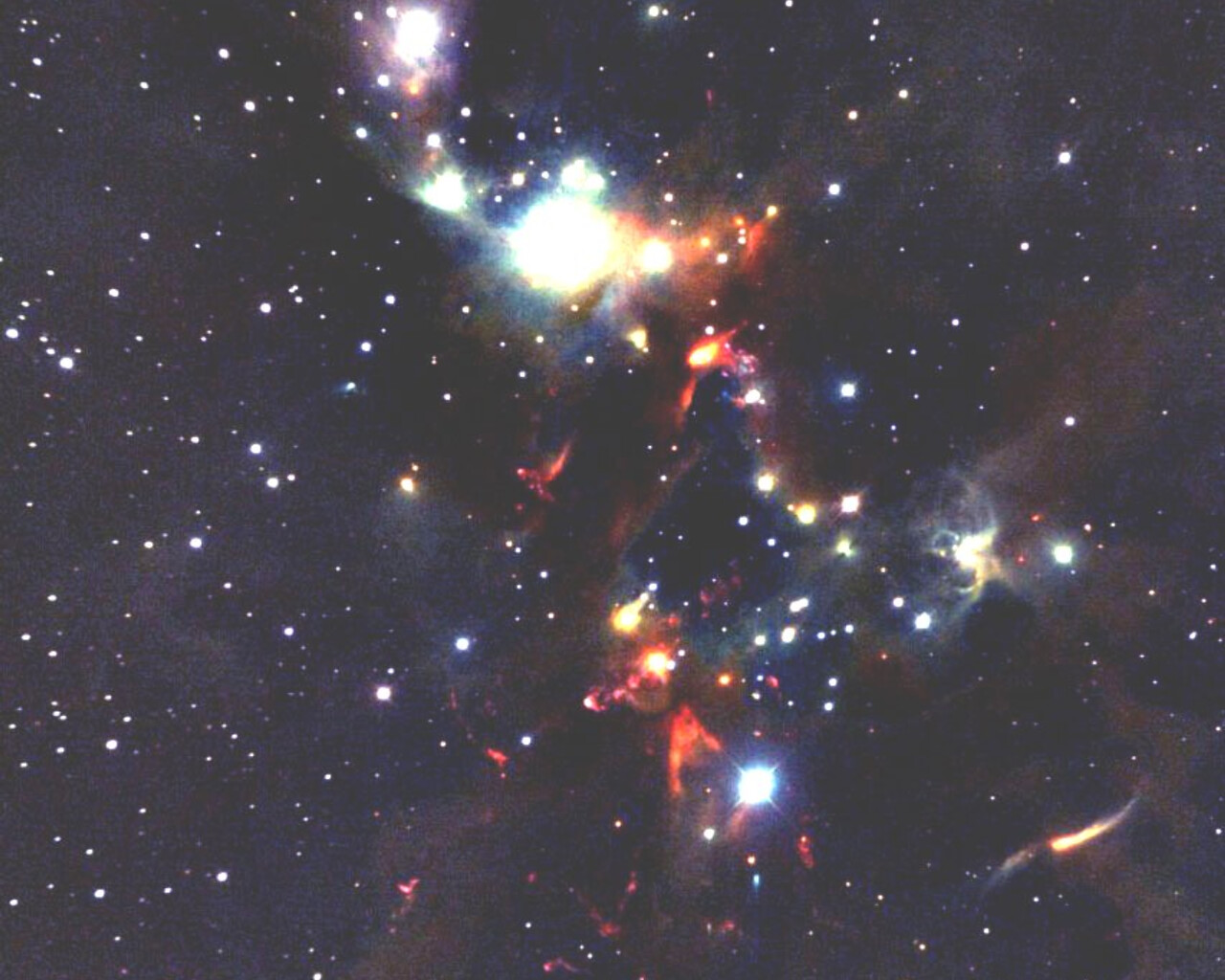
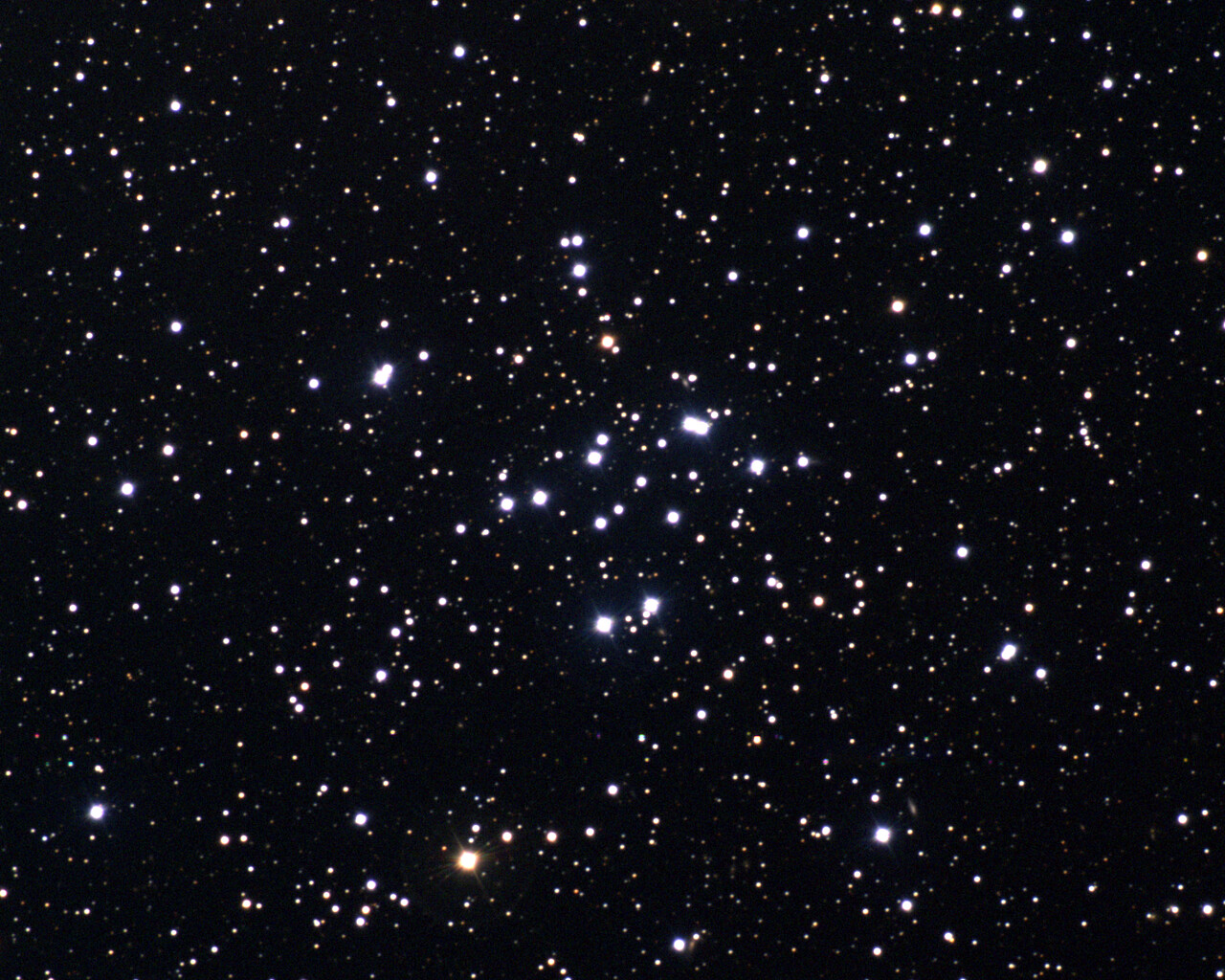
Perseus includes a number of notable objects. NGC 869 and NGC 884 are collectively known as the Double Cluster. The Double Cluster is visible to the naked eye from a dark site and is a wonderful sight through binoculars and wide-field telescopes. The clusters shine at magnitudes 3.7 and 3.8 and lie about 7500 light-years away. Messier 34 is a magnitude-5.5 open cluster about 1500 light-years away. Messier 76 is known as the Little Dumbbell Nebula because of its resemblance to Messier 27. The Little Dumbbell shines at magnitude 10.1 and lies 2500 light-years away. NGC1499 is also known as the California Nebula because of its shape. The California Nebula shines at magnitude 6.0 and lies 1000 light-years away.
The Perseid Meteor Shower peaks in August and is one of the best meteor showers of the year.